Analysis of Students' Intuitive Thinking Abilities in Solving Mathematical Problems on Integer Topics
https://doi.org/10.51574/kognitif.v6i1.4408
Keywords:
Intuitive Thinking Ability , Problem-Solving , Integers , Common Sense , Catalytic Inference , Power of SynthesisAbstract
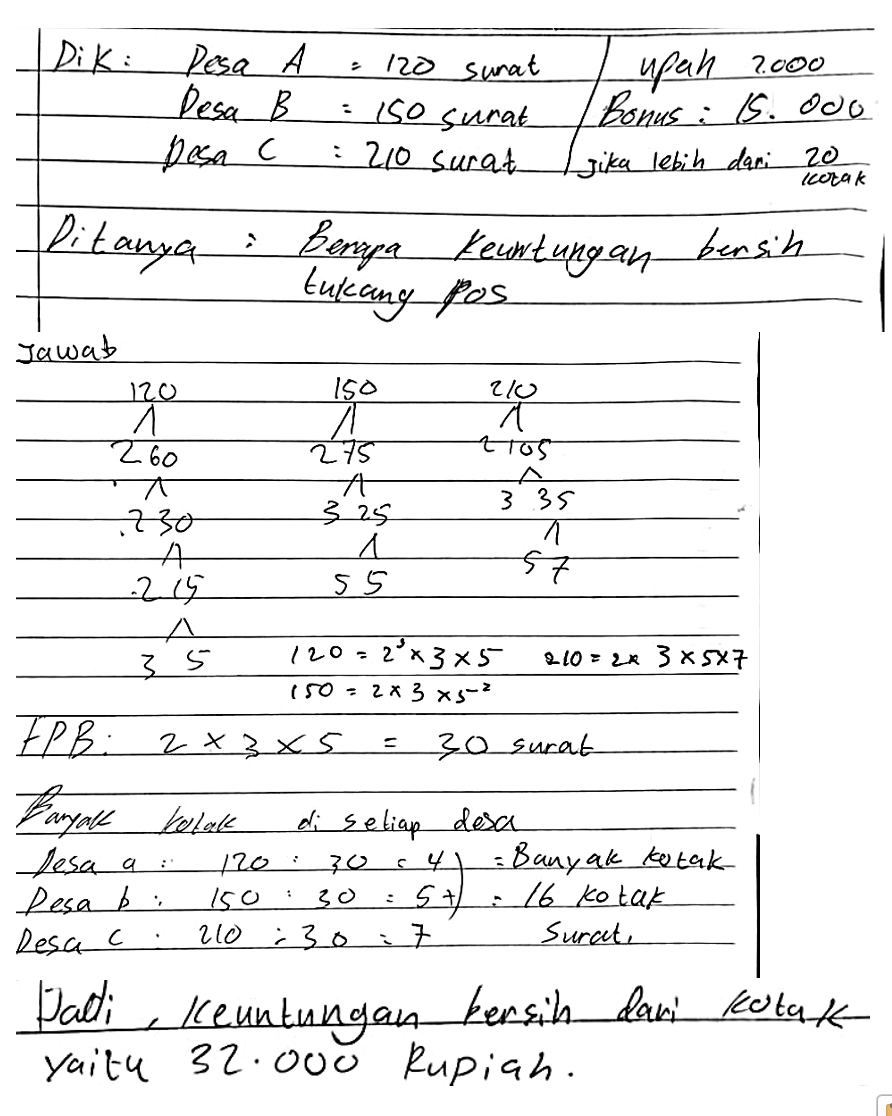
This study aims to analyze and describe students' intuitive thinking abilities in solving mathematical problems on the topic of integers. This research employs a qualitative descriptive method. One research subject (S1) will be selected using purposive sampling based on their ability to demonstrate initial indications of intuitive thinking, such as the accuracy and speed of their initial response to a problem. The research instrument consists of one integer problem-solving test question designed to assess intuitive thinking abilities. Data is collected through triangulation using the think-aloud technique during the problem-solving process, followed by a semi-structured interview to explore the subject's (S1) reasoning and intuitive thought processes. Data is analyzed qualitatively through the stages of data reduction, data presentation, and conclusion drawing. The results reveal that intuition, specifically the common-sense type, acts as a cognitive bridge that accelerates the emergence of ideas and the formulation of problem-solving strategies. This intuitive thinking characteristic is demonstrated through the application of systematic strategies, logical reasoning, and a strong reliance on prior learning experiences. These findings indicate that learning experiences can serve as a crucial foundation in forming effective mathematical intuition. Therefore, mathematics instruction should be designed to enrich student experiences through a variety of problem-solving tasks to develop students' intuitive thinking abilitie
Downloads
References
Badan Pengembangan dan Pembinaan Bahasa. (2025). Kamus Besar Bahasa Indonesia (KBBI) Daring. Kementerian Pendidikan, Kebudayaan, Riset, Dan Teknologi. https://kbbi.kemdikbud.go.id
Davita, P. W. C., & Pujiastuti, H. (2020). Anallisis Kemampuan Pemecahan Masalah Matematika Ditinjau dari Gender. Kreano, Jurnal Matematika Kreatif-Inovatif, 11(1), 110–117. https://doi.org/10.15294/kreano.v11i1.23601
Dewantara, A. H., & Saraswati, S. (2022). Analisis Berpikir Intuitif Siswa dalam Menyelesaikan Masalah Persentase. Didaktika : Jurnal Kependidikan, 15(1), 49–61. https://doi.org/10.30863/didaktika.v15i1.62
Evans, T., Klymchuk, S., Murphy, P. E. L., Novak, J., Stephens, J., & Thomas, M. (2021). Non-routine mathematical problem-solving: creativity, engagement, and intuition of STEM tertiary students. STEM Education, 1(4), 256–278. https://doi.org/10.3934/steme.2021017
Fatima, A. A., & Susanah. (2019). Profil Intuisi Siswa SMP dalam Pemecahan Masalah Matematika Ditinjau dari Gaya Kognitif Reflektif dan Impulsif. 8(3), 550–558.
Fischbein, E. (1987). Intuition in science and mathematics. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 30(4), 372. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0378-4754(98)90009-x
Hadamard, J. (1945). The Psychology of Invention in the Mathematical Field. In A Century in Books: Princeton University Press 1905–2005 (p. 22). https://doi.org/10.2307/2280144
Henden, G. (2004). Intuition and its Role in Strategic Thinking. Series of Dissertations, 1–189.
Lenaini, I. (2021). Teknik Pengambilan Sampel Purposive Dan Snowball Sampling. HISTORIS: Jurnal Kajian, Penelitian & Pengembangan Pendidikan Sejarah, 6(1), 33–39. http://journal.ummat.ac.id/index.php/historis
Miles, M. B., & Huberman, A. M. (1994). Qualitative Data Analysis. SAGE Publications.
Millah, A. S., Apriyani, Arobiah, D., Febriani, E. S., & Ramdhani, E. (2023). Analisis Data dalam Penelitian Tindakan Kelas. Jurnal Kreativitas Mahasiswa, 1(2), 140–153.
Musriroh, R. Z., Hidayanto, E., & Rahardi, R. (2021). Penalaran Spasial Matematis Dimensi Persepsi dan Visualisasi Kelas VIII dalam Pemecahan Masalah Geometri. Jurnal Pendidikan: Teori, Penelitian, Dan Pengembangan, 6(11), 1774. https://doi.org/10.17977/jptpp.v6i11.15144
Mutia, Rochmad, & Isnarto. (2021). Pentingkah Sebuah Intuisi dalam Pembelajaran Matematika? Prisma, 4, 369–374. https://journal.unnes.ac.id/sju/index.php/prisma/
Prameswari, D. A., & Muniri, M. (2023). Karakteristik Berpikir Intuitif Siswa dalam Menyelesaikan Soal Matematika Ditinjau dari Kemampuan Matematika. Lattice Journal : Journal of Mathematics Education and Applied, 3(1), 79. https://doi.org/10.30983/lattice.v3i1.6554
Rifa’i, Y. (2023). Analisis Metodologi Penelitian Kulitatif dalam Pengumpulan Data di Penelitian Ilmiah pada Penyusunan Mini Riset. Cendekia Inovatif Dan Berbudaya, 1(1), 31–37. https://doi.org/10.59996/cendib.v1i1.155
Srimuliati, S., & Wahyuni, W. (2020). Kemampuan Berfikir Intuitif Mahasiswa Calon Guru dalam Penyelesaian Masalah Matematika. Jurnal Ilmiah Pendidikan Matematika Al Qalasadi, 4(2), 98–109. https://doi.org/10.32505/qalasadi.v4i2.2186
Zaporojets, K., Bekoulis, G., Deleu, J., Demeester, T., & Develder, C. (2021). Solving arithmetic word problems by scoring equations with recursive neural networks. Expert Systems with Applications, 174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.114704
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Noera Shikin, Nizlel Huda, Ade Kumalasari

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Education and Talent Development Center of Indonesia (ETDC Indonesia)
e-mail: kognitif@gmail.com, website : https://etdc-indonesia.com

Kognitif: Jurnal Riset HOTS Pendidikan Matematika dengan Situs: https://etdci.org/journal/kognitif berlisensi Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License









.png)

