Impact of the Auditory, Intellectually, and Repetition (AIR) Learning Model on Students’ Mathematical Critical Thinking
https://doi.org/10.51574/kognitif.v6i1.3818
Keywords:
Auditory, Intellectually, and Repetition (AIR) , Mathematical Critical Thinking , Mathematics Learning , 21st-century skills , Quasi-Experimental Design , Instructional InnovationAbstract
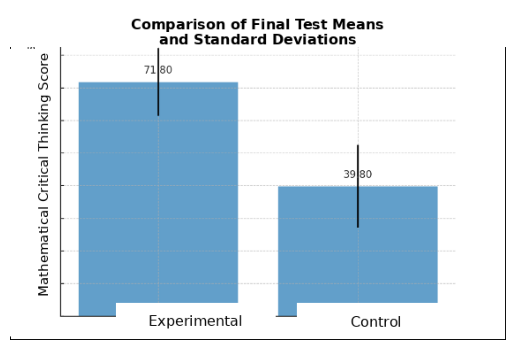
Critical thinking is an essential skill in 21st-century mathematics education; however, Indonesian students still demonstrate low achievement in this domain. Preliminary observations at SMP Negeri 8 Gunungsitoli revealed that students’ mathematical critical thinking skills were not yet optimal, partly due to the predominance of conventional instructional approaches. This study examined the effect of the Auditory, Intellectually, and Repetition (AIR) learning model on students’ mathematical critical thinking skills. A quasi-experimental method with a nonequivalent control group design was employed, involving 60 seventh-grade students divided into an experimental group (n = 30) and a control group (n = 30). The research instrument was an essay-based mathematical critical thinking test consisting of three items, which demonstrated logical and empirical validity and satisfactory reliability. The results indicated that both groups had relatively comparable low baseline performance. After the intervention, the experimental group achieved a mean score of 71.80 (high category), whereas the control group reached only 39.80 (low category). An independent-samples t-test showed that t = 10.683 exceeded ttable = 1.672 (p < 0.05), with a very large effect size (Cohen’s d = 2.76). Simple linear regression analysis indicated that the AIR model accounted for 88.6% of the variance in students’ mathematical critical thinking skills (R² = 0.886). These findings confirm that the AIR learning model effectively enhances mathematical critical thinking by engaging students in listening activities, reflective intellectual processing, and repeated practice. This study contributes theoretically to the development of higher-order thinking-oriented mathematics instruction and offers practical implications for teachers and policymakers in promoting interactive, student-centered learning models.
Downloads
References
Badawi, J. A., Pertiwi, R. P., & Dewi, S. E. K. (2022). Pengaruh Penggunaan Model Pembelajaran Air ( Auditory , Intellectualy , Repetition ) Terhadap Hasil Belajar Matematika Pada Siswa Kelas IV SDN Nusa Tenggara. Jurnal Riset Madrasah Ibtidaiyah (JURMIA), 2(2).
Farida, A., Harisuna, N. R., & Nurida, S. (2019). Modifikasi model pembelajaran auditory intelectualy repetition dengan strategi pembelajaran tugas dan paksa. Prosiding Seminar Nasional Pendidikan KALUNI, 2. https://doi.org/10.30998/prokaluni.v2i0.101
Gultom, L. N., & Zuardi, Z. (2025). Peningkatan Hasil Belajar Peserta Didik pada Pembelajaran IPAS dengan Menggunakan Model Cooperative Learning Tipe Auditory Intellectually Repetition (AIR) di Kelas IV SDN 03 Geragahan Kabupaten Agam. TSAQOFAH, 5(4). https://doi.org/10.58578/tsaqofah.v5i4.6199
Habibi, H., & Suparman, S. (2020). Literasi Matematika dalam Menyambut PISA 2021 Berdasarkan Kecakapan Abad 21. JKPM (Jurnal Kajian Pendidikan Matematika), 6(1), 57. https://doi.org/10.30998/jkpm.v6i1.8177
Hartmann, L. M., Schukajlow, S., Niss, M., & Jankvist, U. T. (2024). Preservice teachers’ metacognitive process variables in modeling-related problem posing. Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 76(September), 101195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmathb.2024.101195
Hobri, Sahnawi, Susanto, & Ridlo, Z. R. (2021). The impact of implementing auditory intellectually repetition (air) learning model based on learning community for students’ creative thinking skills. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 1832(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1832/1/012035
Huda, S., Munifah, Syazali, M., Rahayu, S. S., & Umam, R. (2020). The effectiveness of two stay two stray, somatic, auditory, visualization, intellectually, and auditory learning to improving numerical ability. Humanities & Social Sciences Reviews, 8(4). https://doi.org/10.18510/hssr.2020.8442
Jami Ahmad Badawi, Ratih Purnama Pertiwi, & Sri Enggar Kencana Dewi. (2022). Pengaruh Penggunaan Model Pembelajaran Air (Auditory, Intellectualy, Repetition) Terhadap Hasil Belajar Mata Pelajaran Matematika Pada Siswa Kelas IV SDN Nusa Tenggara. Jurnal Riset Madrasah Ibtidaiyah (JURMIA), 2(2). https://doi.org/10.32665/jurmia.v2i2.322
Kartika, H. I., H, H., & Selegi, S. F. (2023). The impact of the auditory, intellectually, repetition (Air) model on social studies learning outcomes. Indonesian Journal of Primary Education, 7(1). https://doi.org/10.17509/ijpe.v7i1.37002
Kuntze, S., Aizikovitsh-Udi, E., & Clarke, D. (2017). Hybrid task design: connecting learning opportunities related to critical thinking and statistical thinking. ZDM - Mathematics Education, 49(6), 923–935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-017-0874-4
Lehmann, T. H. (2023). Using algorithmic thinking to design algorithms: The case of critical path analysis. Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 71(August 2022), 101079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmathb.2023.101079
Lestari, F. P., Ahmadi, F., & Rochmad, R. (2021). The implementation of mathematics comic through contextual teaching and learning to improve critical thinking ability and character. European Journal of Educational Research, 10(1). https://doi.org/10.12973/EU-JER.10.1.497
Ødegaard, R. P., Arnesen, K. K., & Langfeldt, M. B. (2024). Tools to support learning to plan discussions that promote students’ mathematical reasoning. Journal of Mathematics Teacher Education, (1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10857-024-09668-w
OECD. (2018). Programme for International Students Assesment (PISA) Result From PISA 2018.
Rambe, A. H., & Aisyah, S. (2023). Correlation of auditory, intellectually, repetition (air) learning models on student achievement. Molang: Journal Of Islamic Education, 1(01). https://doi.org/10.32806/c6evca15
Riyayani, L. (2021). Peningkatan Prestasi Belajar Materi Pemahaman Ide Pokok Dalam Teks Melalui Penerapan Model Pembelajaran Auditory, Intellectually and Repetition (AIR). Journal on Education, 3(01). https://doi.org/10.31004/joe.v3i01.355
Safrudiannur, & Rott, B. (2019). The different mathematics performances in PISA 2012 and a curricula comparison: enriching the comparison by an analysis of the role of problem solving in intended learning processes. Mathematics Education Research Journal, 31(2), 175–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13394-018-0248-4
Salay, R. (2019). Perbedaan Motivasi Belajar Siswa yang Mendapatkan Teacher Centered Learning (TCL) Dengan Student Centered Learning (SCL). Education, 1(1), 1–12.
Sormunen, K., Juuti, K., & Lavonen, J. (2020). Maker-Centered Project-Based Learning in Inclusive Classes: Supporting Students’ Active Participation with Teacher-Directed Reflective Discussions. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 18(4), 691–712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-019-09998-9
Stockero, S. L., Leatham, K. R., Ochieng, M. A., Van Zoest, L. R., & Peterson, B. E. (2020). Teachers’ orientations toward using student mathematical thinking as a resource during whole-class discussion. In Journal of Mathematics Teacher Education (Vol. 23, Number 3). Springer Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10857-018-09421-0
Yasin, M., Jauhariyah, D., Madiyo, M., Rahmawati, R., Farid, F., Irwandani, I., & Mardana, F. F. (2019). The guided inquiry to improve students mathematical critical thinking skills using student’s worksheet. Journal for the Education of Gifted Young Scientists, 7(4), 1345–1360. https://doi.org/10.17478/jegys.598422
Zanden, P. J. A. C. Van Der, Denessen, E., Cillessen, A. H. N., Meijer, P. C., Zanden, P. J. A. C. Van Der, Denessen, E., & Cillessen, A. H. N. (2020). Fostering critical thinking skills in secondary education to prepare students for university : teacher perceptions and practices. Research in Post-Compulsory Education, 25(4), 394–419. https://doi.org/10.1080/13596748.2020.1846313
Zulkardi, Meryansumayeka, Putri, R. I. I., Alwi, Z., Nusantara, D. S., Ambarita, S. M., Maharani, Y., & Puspitasari, L. (2020). How students work with pisa-like mathematical tasks using covid-19 context. Journal on Mathematics Education, 11(3), 405–416. https://doi.org/10.22342/jme.11.3.12915.405-416
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Indah Natalia Harefa, Yakin Niat Telaumbanua, Ratna Natalia Mendrofa, Netti Kariani Mendrofa

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Education and Talent Development Center of Indonesia (ETDC Indonesia)
e-mail: kognitif@gmail.com, website : https://etdc-indonesia.com

Kognitif: Jurnal Riset HOTS Pendidikan Matematika dengan Situs: https://etdci.org/journal/kognitif berlisensi Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License









.png)

