Enhancing Students’ Learning Outcomes through the Guided Inquiry Learning Model in Trigonometry
https://doi.org/10.51574/kognitif.v5i3.3083
Keywords:
Guided Inquiry , Learning Outcomes , Classroom Action Research (CAR)Abstract
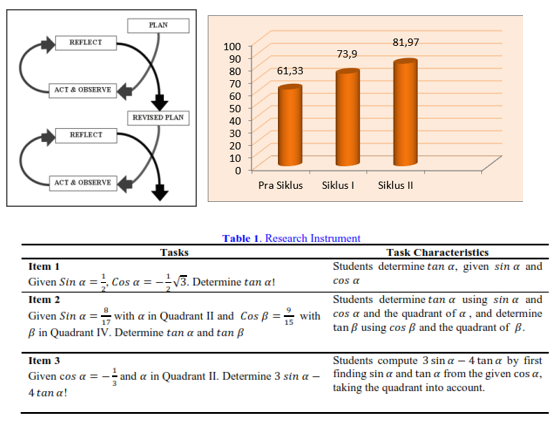
Learning trigonometry remains a challenge for many students due to teacher-centered instruction and limited opportunities for conceptual exploration. This issue highlights the urgency of implementing innovative learning models that actively engage students in constructing their understanding. This study aimed to improve students’ learning outcomes in trigonometry through the Guided Inquiry learning model. The research was conducted as Classroom Action Research (CAR) in two cycles, each consisting of two meetings, involving 30 Grade X vocational school students in Denpasar. Data were collected using essay tests to measure students’ competence in trigonometry and analyzed quantitatively based on cognitive test results. The findings showed a steady improvement in learning outcomes: prior to the intervention, only 46.67% of students achieved mastery with an average score of 61.33; in Cycle I, mastery increased to 66.67% with an average score of 73.90; and in Cycle II, mastery reached 80% with an average score of 81.97. These results indicate that the Guided Inquiry learning model effectively enhanced students’ understanding of trigonometric concepts and overall learning achievement. This improvement was influenced by the implementation of the Guided Inquiry learning model syntax, which encouraged students to develop a deeper understanding of trigonometry concepts. Therefore, it can be concluded that the Guided Inquiry learning model is effective in enhancing students’ learning outcomes.
Downloads
References
Afandi, M. (2021). Cara Efektif Menulis Karya Imiah Seting Penelitian Tindakan Kelas Pendidikan Dasar dan Umum. Kesatu. Bandung: CV Alfabeta.
Ariesta, P. N ., & Awalludin, S. A. (2021). Pengaruh Model Pembelajaran Penemuan Terbimbing Berbantuan LKPD Terhadap Kemampuan Komunikasi Matematis Siswa. Journal of Authentic Research on Mathematics Education (JARME), 3(1). https://doi.org/10.37058/jarme.v3i1.2427
Arrosyad, M. I., Wahyuni, E., Kirana, D., & Sartika, M. (2023). Analisis Faktor yang Mempengaruhi Rendahnya Hasil Belajar Siswa Sekolah Dasar Dalam Penyelesaian Soal Cerita Matematika. Educativo: Jurnal Pendidikan, 2(1), 222–228. https://doi.org/10.56248/educativo.v2i1.138
Artigue, M., & Blomhøj, M. (2013). Conceptualizing inquiry-based education in mathematics. ZDM Mathematics Education, 45(6), 797–810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-013-0506-6
Astuti, W., & Jannah, M. (2022). Penerapan Model Pembelajaran Inkuiri Terbimbing untuk Meningkatkan Motivasi dan Hasil Belajar Matematika Siswa SMP. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 10(1), 55–62.
Ayu, S., Ardianti, S. D., & Wanabuliandari, S. (2021). Analisis Faktor Penyebab Kesulitan Belajar Matematika. Jurnal Program Studi Pendidikan Matematika, 10(3). https://doi.org/10.24127/ajpm.v10i3.3824
Bruner, J. S. (1961). The act of discovery. Harvard Educational Review, 31(1), 21–32.
Cholid, Ahmadi, & Oktaviani. (2022). Analisis Pemahaman Konsep Matematis Pada Siswa Kelas X Pada Materi Perbandingan Trigonometri Menggunakan Model Pembelajaran Discovery Learning. Teorema: Teori dan Riset Matematika, 7(1), 89–100. http://dx.doi.org/10.25157/teorema.v7i1.5720
Fahmia, H., Karjiyati, V., & Dalifa, D. (2020). Pengaruh Model Guided Inquiry Terhadap Hasil Belajar Siswa Pada Pembelajaran Matematika Siswa SD Kota Bengkulu. Juridikdas (Jurnal Riset Pendidikan Dasar), 2(3), 237–244. https://doi.org/10.33369/Juridikdas.2.3.237-244
Fernando, Y., Andriani, P., & Syam, H. (2024). Pentingnya Motivasi Belajar Dalam Meningkatkan Hasil Belajar Siswa. Journal of Educational and Inspiration, 2(3), 61–68. https://doi.org/10.59246/Alfihris.V2i3.843
Hartati, P. (2019). Peningkatan Hasil Belajar Matematika Siswa SMA Melalui Pembelajaran Guided Inquiry. Jurnal Penelitian Pembelajaran Matematika Sekolah (JP2MS), 3(2), 269–274. https://doi.org/10.33369/Jp2ms.3.2.269-274
Hasanah, U., Masitoh, S., Dealova, Z. K., Yunus, M., Frimananda, G. R., & Prihantini, P. (2025). Faktor Penunjang Keberhasilan Dalam Proses Pembelajaran Siswa Sekolah Dasar. Jurnal Review Pendidikan dan Pengajaran (JRPP), 8(1), 1184–1188.
Hmelo-Silver, C. E. (2004). Problem-based learning: What and how do students learn? Educational Psychology Review, 16(3), 235–266. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EDPR.0000034022.16470.f3
Kuhlthau, C. C., Maniotes, L. K., & Caspari, A. K. (2015). Guided inquiry: Learning in the 21st century (2nd ed.). ABC-CLIO.
Marhaeni, L. P. E. (2020). Penerapan Model Pembelajaran Inkuiri Terbimbing Sebagai Upaya Meningkatkan Prestasi Belajar Matematika Siswa SMP. Journal of Education Technology, 4(1), 11–16. https://doi.org/10.23887/Jet.V4i1.23739
Marto, H., Ruknan, & Insiano, D. A. (2023). Model Pembelajaran Guided Inquiry dalam Meningkatkan Keterampilan Proses Sains Dasar Siswa SMA. Pekalongan: NEM.
Nastiti, F. F., & Syaifudin, A. H. (2020). Hubungan Pemahaman Konsep Matematis Terhadap Hasil Belajar Siswa Kelas VIII SMP N 1 Plosoklaten Pada Materi Lingkaran. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 4(1), 8–15. http://dx.doi.org/10.33087/phi.v4i1.80
National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM). (2000). Principles and standards for school mathematics. Reston, VA: The National Council of Teachers of Mathematics Inc.
OECD. (2023). PISA 2022 results (Volume I): The state of learning and equity in education (PISA, Ed.; Vol. 1). OECD Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1787/1f0960c6-en
Pedaste, M., Mäeots, M., Siiman, L. A., de Jong, T., van Riesen, S. A. N., Kamp, E. T., Manoli, C. C., Zacharia, Z. C., & Tsourlidaki, E. (2015). Phases of inquiry-based learning: Definitions and the inquiry cycle. Educational Research Review, 14, 47–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2015.02.003
Permendikbud Nomor 22 Tahun 2016 tentang Standar Proses Pendidikan Dasar dan Menengah.
Prince, M. J., & Felder, R. M. (2006). Inductive teaching and learning methods: Definitions, comparisons, and research bases. Journal of Engineering Education, 95(2), 123–138. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2168-9830.2006.tb00884.x
Purba, P. B., Mawati, A. T., Kuswandi, J. S., Hulu, I. L., Sitopu, J. W., Pasaribu, A. N., Yuniwati, I., & Masrul. (n.d.). Penelitian Tindakan Kelas. Medan: Yayasan Kita Menulis.
Purwanto. (2013). Evaluasi Hasil Belajar. Yogyakarta: Pustaka Belajar.
Rahayu, F. (2019). Efektivitas Self Efficacy Dalam Mengoptimalkan Kecerdasan Dan Prestasi Belajar Peserta Didik. Consilia: Jurnal Ilmiah Bimbingan Dan Konseling, 2(2), 119–129. https://doi.org/10.33369/consilia.2.2.119-129
Segara, B., Choirudin, C., Setiawan, A., Saidun Anwar, M., & Arif, V. R. (2023). Metode Inquiry: Meningkatkan Hasil Belajar Matematika Siswa SMP Pada Materi Luas Bangun Datar. Jurnal Penelitian Tindakan Kelas, 1(1), 18–22. https://doi.org/10.61650/jptk.v1i1.48
Skinner, B. F. (1958). Teaching machines. Science, 128(3330), 969–977. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.128.3330.969
Sudijono, A. (1996). Pengantar Evaluasi Pendidikan. Jakarta: PT Raja Grafindo Persada.
Sudjana, N. (2017). Penilaian Hasil Proses Belajar Mengajar. Bandung: PT Remaja Rosdakarya.
Sundari, F. S., & Indrayani, E. (2019). Penerapan Model Pembelajaran Inkuiri Terbimbing Untuk Meningkatkan Hasil Belajar Matematika. Jurnal Pendidikan dan Pengajaran Guru Sekolah Dasar, 2(2), 72–75. https://doi.org/10.55215/jppguseda.v2i2.1449
Suparman, A., & Rahayu, D. (2021). Model inkuiri terbimbing dalam meningkatkan kemampuan pemecahan masalah matematika. Jurnal Inovasi Pendidikan Matematika, 7(2), 98–105.
Syaifuddin, & Iswara, A. (2022). Pengembangan Model Pembelajaran Berbasis Guided Inquiry dengan Menggunakan Media Matlab. Malang: Media Nusa Creative.
Yanuar, A., & Pius, I. (2023). Upaya Meningkatkan Keaktifan dan Hasil Belajar Siswa Kelas 4 SDK Wignya Mandala Melalui Pembelajaran Kooperatif. Jurnal Kateketik dan Pastoral, 8(1). https://doi.org/10.53544/sapa.v8i1.327
Zainal, A. (2008). Penelitian Tindakan Kelas. Bandung: CV Yarma Widya.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Amanatul Hidayah, Kadek Adi Wibawa, Marius Simons

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Education and Talent Development Center of Indonesia (ETDC Indonesia)
e-mail: kognitif@gmail.com, website : https://etdc-indonesia.com

Kognitif: Jurnal Riset HOTS Pendidikan Matematika dengan Situs: https://etdci.org/journal/kognitif berlisensi Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License









.png)

