Bio-Math Synergy: Creating Relevant Cross-Disciplinary Learning in the Digital Age
https://doi.org/10.51574/ijrer.v5i1.4701
Keywords:
Bio-Math Synergy, Digital Simulation, High School Students, Interdisciplinary Learning, Numeracy LiteracyAbstract
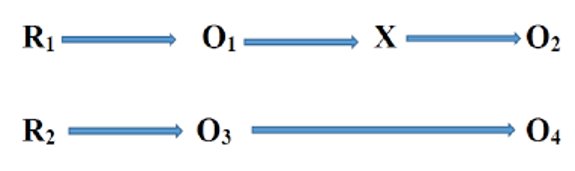
High school learning is generally divided into isolated subjects, with biology deemed rote learning and math as formulas with no practical value. In the data-driven digital age, high school students find it difficult to connect statistical or algebraic concepts to biological events like the spread of viruses and changes in ecosystems. Lack of connection between these fields reduces computational thinking and scientific literacy. This study examines whether the "Bio-Math Synergy" learning model improves high school students' transdisciplinary comprehension. The study used computerized techniques to incorporate ecology, genetics, function modeling, and basic statistics. This quasi-experimental study used pretest-posttest control groups. Eleventh graders from two Wajo Regency high schools studied. The experimental class utilized the "Bio-Math Synergy" model to analyze biology lab data through an interactive simulation platform and spreadsheets, while the control class employed traditional learning methods. The findings indicated the experimental class had much higher numeracy literacy results than the control class. Students learn that biology requires mathematics by modeling bacterial development and Mendel's rules digitally. Because STEM education felt more relevant to contemporary technology, an interest poll showed a 40% rise in student excitement for STEM jobs. This article provides a practical module for high school teachers to apply biology-math project-based learning (PjBL). This study supports digital-era education approaches that encourage critical thinking and cross-disciplinary problem-solving for Generation Z.
References
Abdi, G., Jain, M., Barwant, M., Tendulkar, R., Tendulkar, M., Tariq, M., & Amir, A. (2024). Unveiling the dynamic role of bioinformatics in automation for efficient and accurate data processing and interpretation. In Advances in Bioinformatics (pp. 279-319). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8401-5_15
Aini, V., Hidayat, T., Kusnadi, K., Williams, C., & Hadibarata, T. (2024). Analysis numeracy literacy skills of high school students in biodiversity material based on minimum competency assessment questions. Jurnal Pendidikan IPA Indonesia, 13(1), 128-136. https://doi.org/10.15294/jpii.v13i1.49265
Almuhanna, M. A. (2025). Teachers' perspectives of integrating AI-powered technologies in K-12 education for creating customized learning materials and resources. Education and Information Technologies, 30(8), 10343-10371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-024-13257-y
Anđić, B., Lavicza, Z., Ulbrich, E., Cvjetićanin, S., Petrović, F., & Maričić, M. (2024). Contribution of 3D modelling and printing to learning in primary schools: a case study with visually impaired students from an inclusive Biology classroom. Journal of Biological Education, 58(4), 795-811. https://doi.org/10.1080/00219266.2022.2118352
Bell, E., Provost, J., & Bell, J. K. (2019). Skills and foundational concepts for biochemistry students. In Biochemistry education: From theory to practice (pp. 65-109). American Chemical Society. https://doi.org/10.1021/bk-2019-1337.ch004
Borovik, A. (2021). A mathematician’s view of the unreasonable ineffectiveness of mathematics in biology. Biosystems, 205, 104410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystems.2021.104410
Christensen, D., & Lombardi, D. (2020). Understanding biological evolution through computational thinking: A K-12 learning progression. Science & Education, 29(4), 1035-1077. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11191-020-00141-7
Clemson, M., Huang, A., Denyer, G., & Costabile, M. (2025). Teaching second‐year biochemistry students the principles of an enzyme‐catalyzed spectrophotometric assay with an online lab simulator. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmb.21903
Cornish-Bowden, A., & Hofmeyr, J. H. S. (2002). The role of stoichiometric analysis in studies of metabolism: an example. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 216(2), 179-191. https://doi.org/10.1006/jtbi.2002.2547
dos Santos Carmo, J., & Crescenti, E. P. (2022). Mathematics anxiety and successful reversal strategies: A Brazilian experience. In Handbook of Stress and Academic Anxiety: Psychological Processes and Interventions with Students and Teachers (pp. 115-126). Cham: Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-12737-3_8
Flanigan, A. E., & Babchuk, W. A. (2022). Digital distraction in the classroom: Exploring instructor perceptions and reactions. Teaching in Higher Education, 27(3), 352-370. https://doi.org/10.1080/13562517.2020.1724937
Gordon, S. P., Gross, S., Bahamonde, M., Winn, J., Seifert, J., Martin, C. A., & Yang, Y. (2022). Developing a mathematics curriculum for the biosciences. Primus, 32(2), 218-245. https://doi.org/10.1080/10511970.2021.1919258
Holmes, S. H., & Huber, W. (2018). Modern statistics for modern biology. Cambridge university press.
Kantaros, A., Ganetsos, T., Pallis, E., & Papoutsidakis, M. (2025). From Mathematical Modeling and Simulation to Digital Twins: Bridging Theory and Digital Realities in Industry and Emerging Technologies. Applied Sciences, 15(16), 9213. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169213
Kokkonen, T., & Schalk, L. (2021). One instructional sequence fits all? A conceptual analysis of the applicability of concreteness fading in mathematics, physics, chemistry, and biology education. Educational Psychology Review, 33(3), 797-821. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-020-09581-7
Lane, P. A. (2024). Robert Rosen’s relational biology theory and his emphasis on non-algorithmic approaches to living systems. Mathematics, 12(22), 3529. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12223529
Marhami, M., Juandi, D., & Dasari, D. (2024). Indonesian students’ numeracy skills based on PISA mathematical problems in secondary school: A meta-synthesis. Jurnal Pendidikan MIPA, 25(1), 14-26. https://doi.org/10.23960/jpmipa/v25i1.pp14-26
Martin, F., Long, S., Haywood, K., & Xie, K. (2025). Digital distractions in education: a systematic review of research on causes, consequences and prevention strategies. Educational technology research and development, 1-29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-025-10550-6
Megawati, L. A., & Sutarto, H. (2021). Analysis numeracy literacy skills in terms of standardized math problem on a minimum competency assessment. Unnes Journal of Mathematics Education, 10(2), 155-165. https://doi.org/10.15294/ujme.v10i2.49540
Müller, F. A., & Wulf, T. (2024). Differences in learning effectiveness across management learning environments: A cognitive load theory perspective. Journal of Management Education, 48(4), 802-828. https://doi.org/10.1177/10525629231200206
Nurqamar, D., & Nur, I. R. D. (2022). Comparative Study of Indonesian Students' Mathematical Literacy Abilities with Other Countries in Terms of PISA Type HOTS. EduMa: Mathematics education learning and teaching, 11(1), 45-56. http://dx.doi.org/10.24235/eduma.v11i1.9924
Rozenszajn, R., & Yarden, A. (2014). Mathematics and biology teachers’ tacit views of the knowledge required for teaching: varying relationships between CK and PCK. International Journal of STEM Education, 1(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-014-0011-7
Shahidi Hamedani, S., Aslam, S., Mundher Oraibi, B. A., Wah, Y. B., & Shahidi Hamedani, S. (2024). Transitioning towards tomorrow’s workforce: Education 5.0 in the landscape of society 5.0: A systematic literature review. Education Sciences, 14(10), 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci14101041
Shambare, B., & Simuja, C. (2022). A critical review of teaching with virtual lab: A panacea to challenges of conducting practical experiments in science subjects beyond the COVID-19 pandemic in rural schools in South Africa. Journal of Educational Technology Systems, 50(3), 393-408. https://doi.org/10.1177/00472395211058051
Skulmowski, A., & Xu, K. M. (2022). Understanding cognitive load in digital and online learning: A new perspective on extraneous cognitive load. Educational psychology review, 34(1), 171-196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-021-09624-7
Sweller, J. (2020). Cognitive load theory and educational technology. Educational technology research and development, 68(1), 1-16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-019-09701-3
Tan, A. L., Ong, Y. S., Ng, Y. S., & Tan, J. H. J. (2023). STEM problem solving: Inquiry, concepts, and reasoning. Science & Education, 32(2), 381-397. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11191-021-00310-2
Torre-Bastida, A. I., Diaz-de-Arcaya, J., Osaba, E., Muhammad, K., Camacho, D., & Del Ser, J. (2025). Bio-inspired computation for big data fusion, storage, processing, learning and visualization: state of the art and future directions. Neural Computing and Applications, 37(28), 23097-23127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06332-9
Uitto, A., & Saloranta, S. (2017). Subject teachers as educators for sustainability: A survey study. Education Sciences, 7(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci7010008
Weaver, K. F., Morales, V. C., Dunn, S. L., Godde, K., & Weaver, P. F. (2017). An introduction to statistical analysis in research: with applications in the biological and life sciences. John Wiley & Sons.
Ziatdinov, R., Atteraya, M. S., & Nabiyev, R. (2024). The fifth industrial revolution as a transformative step towards society 5.0. Societies, 14(2), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc14020019
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Fitri Fitri, Muhammad Hasbi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.

























