Gender Differences in the Relationship Between Mathematical Disposition and Problem-Solving Skills
https://doi.org/10.51574/kognitif.v5i4.3292
Keywords:
Comparative–Correlational Design , Gender , Mathematical Disposition , Problem-Solving SkillsAbstract
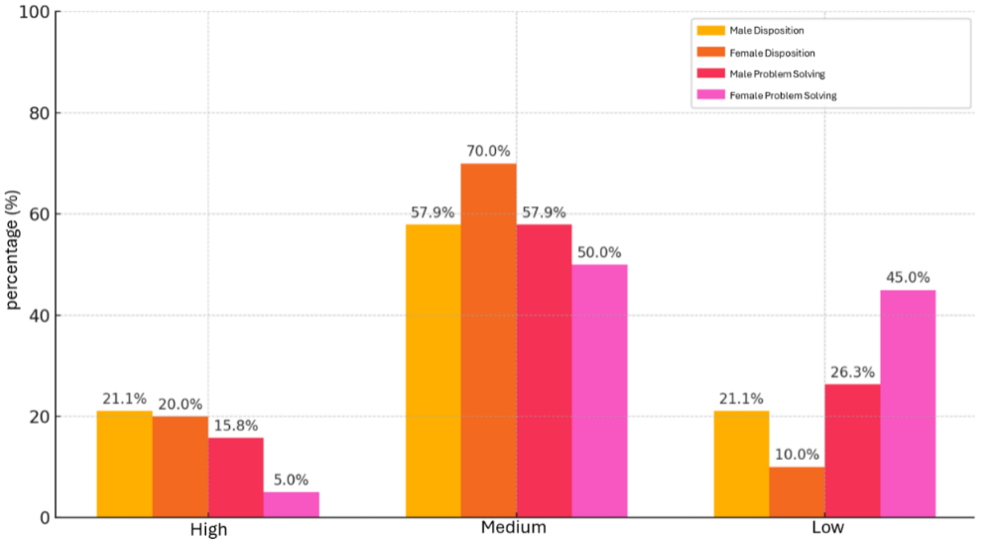
Mathematical disposition, which encompasses students’ confidence, perseverance, curiosity, and appreciation toward mathematics, plays a significant role in shaping their approaches to problem-solving. This study aims to investigate gender-based differences in students’ mathematical disposition and problem-solving ability, and to analyze the overall relationship between these variables. A quantitative approach employing a comparative–correlational design was used. Following Yount’s sampling guideline, 10% of the population (comprising 39 seventh-grade students) was randomly selected through simple random sampling. Research instruments included a Likert-scale questionnaire to measure mathematical disposition and an essay-based test developed from the IDEAL problem-solving framework. Both instruments were previously validated and tested for reliability to ensure data accuracy. Data were analyzed using an independent-samples t-test and Spearman’s rank correlation. Results revealed no significant difference in mathematical disposition between male (M = 67.26) and female students (M = 65.65), t(37) = 0.553, p > 0.05. In contrast, a significant difference was found in problem-solving ability, with male students (M = 69.42) outperforming females (M = 56.70), t(37) = 2.77, p < 0.05. Moreover, a low positive correlation (ρ = 0.2172) was observed between mathematical disposition and problem-solving ability. These findings suggest that gender factors may influence students’ cognitive and affective engagement in mathematical problem-solving. The study contributes to the growing body of research on mathematics education by emphasizing the importance of integrating affective and cognitive dimensions in designing more personalized and effective teaching practices
Downloads
References
Aisyah, A. S., & Novitasari, P. (2023). The Students’ Mathematic Problem Solving Profile Reviewed On Gender Differences. Al Khawarizmi: Jurnal Pendidikan Dan Pembelajaran Matematika, 7(2), 87–94. https://doi.org/10.22373/jppm.v7i2.20821
Barbera, J., Naibert, N., Komperda, R., & Pentecost, T. C. (2021). Clarity on Cronbach’s Alpha Use. Journal of Chemical Education, 98(2), 257–258. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.0c00183
Boman, B., & Wiberg, M. (2024). Cognitive ability, gender, and well-being in school contexts: longitudinal evidence from Sweden. Frontiers in Psychology, 15(9), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1396682
Bransford, J. D., & Stein, B. S. (1993). The IDEAL problem solver: A guide for improving thinking, learning, and creativity (2nd editio). New York: W.H. Freeman.
Çelik, H. C., & Özdemir, F. (2020). Mathematical Thinking as a Predictor of Critical Thinking Dispositions of Pre-service Mathematics Teachers. International Journal of Progressive Education, 16(4), 81–98. https://doi.org/10.29329/ijpe.2020.268.6
Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2018). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches. SAGE Publications, Inc (Fifth Edit). https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429469237-3
Fioriti, C. M., Martell, R. N., Daker, R. J., Malone, E. P., Sokolowski, H. M., Green, A. E., … Lyons, I. M. (2024). Examining the Interplay between the Cognitive and Emotional Aspects of Gender Differences in Spatial Processing. Journal of Intelligence, 12(3), 1–23. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence12030030
Fitri, L., & Hasyim, M. (2018). Pengaruh Kemampuan Disposisi Matematis, Koneksi Matematis, Dan Penalaran Matematis Terhadap Kemampuan Pemecahan Masalah Matematika. JP2M (Jurnal Pendidikan Dan Pembelajaran Matematika), 4(1), 47–60. https://doi.org/10.29100/jp2m.v4i1.1778
Gallagher, A., De Lisi, R., Holst, P., Lisi, A., Morely, M., & Laitusis, C. (2000). Gender Differences in Advanced Mathematical Problem Solving. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 75, 165–190. https://doi.org/10.1006/jecp.1999.2532
Hutajulu, M., Wijaya, T. T., & Hidayat, W. (2019). The Effect of Mathematical Dispositionand Learning Motivation on Problem Solving: An Analysis. Infinity Journal, 8(2), 229–238. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v8i2.p229-238
Juniati, D., & Manoy, J. T. (2025). Exploring the interplay between abductive reasoning and mathematical problem-solving : the role of adversity quotient and gender in middle school students. Perspective of Science and Education (PSE) Journal, 2(4), 243–256. https://pnojournal.wordpress.com/2025/04/30/nasruddin/
Khedidja, D. D., & Moussa, T. (2022). Test for Linearity in Non-Parametric Regression Models. Austrian Journal of Statistics, 51(1), 16–34. https://doi.org/10.17713/ajs.v51i1.1047
Lestari, I., & Andinny, Y. (2023). Kemampuan Pemecahan Masalah Matematika melalui Disposisi Matematika. Griya Journal of Mathematics Education and Application, 3(3), 507–514. https://doi.org/10.29303/griya.v3i3.357
Marynets, K., & Pantova, D. (2024). Successive approximations and interval halving for fractional BVPs with integral boundary conditions. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 436(5), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cam.2023.115361
Massen, J. J. M., Behrens, F., Martin, J. S., Stocker, M., & Brosnan, S. F. (2019). A comparative approach to affect and cooperation. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 107(9), 370–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2019.09.027
OECD. (2023a). PISA 2022 Mathematics Framework. Paris. https://doi.org/ doi.org/10.1787/dfe0bf9c-en
OECD. (2023b). PISA 2022 Results Factsheets Indonesia PUBE, pp. 1–9. Retrieved from https://oecdch.art/a40de1dbaf/C108
Okwonu, F. Z., Asaju, B. L., & Arunaye, F. I. (2020). Breakdown Analysis of Pearson Correlation Coefficient and Robust Correlation Methods. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 917(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/917/1/012065
Pratiwi, A. R., Mulyono, & Supriyono. (2018). Analisis Kemampuan Pemecahan Masalah Berdasarkan Disposisi Matematis Peserta Didik dalam Setting Model Anchored Instruction. Unnes Journal of Mathematics Education, 5(3), 173–181. Retrieved from http://journal.unnes.ac.id/sju/index.php/ujme
Putri, A. G. E., Priyadi, R., & Khoirunnisa. (2023). Perbedaan disposisi matematika siswa yang mengikuti kursus dan tidak mengikuti kursus: mana yang lebih baik? JPMI: Jurnal Pembelajaran Matematika Inovatif, 6(4), 1505–1512. https://doi.org/10.22460/jpmi.v6i4.17301
Rana, J., Gutierrez, P. L. L., & Oldroyd, J. (2021). Quantitative Methods. Global Encyclopedia of Public Administration, Public Policy, and Governance, 12(6), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-31816-5
Sa’Dijah, C., Sa’Diyah, M., Sisworo, & Anwar, L. (2020). Students’ mathematical dispositions towards solving HOTS problems based on FI and FD cognitive style. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2215(April), 060025-1-060025–060028. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0000644
Shen, C., Panda, S., & Vogelstein, J. T. (2022). The Chi-Square Test of Distance Correlation. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 31(1), 254–262. https://doi.org/10.1080/10618600.2021.1938585
Sugiyono. (2017). Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif, Kualitatif, dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta, CV. Retrieved from https://massugiyantojambi.wordpress.com/2011/04/15/teori-motivasi/
Susilo, B. E., Darhim, D., & Prabawanto, S. (2020). Critical thinking skills based on mathematical dispositions in problem-based learning. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series (Vol. 1567, pp. 1–8). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1567/2/022101
Tian, Y., & Cao, N. (2023). Case Study on the Application of Information Technology in Physical Education Teaching Based on Independent Sample T test. In 3rd International Conference on Information Technology and Contemporary Sports (TCS) (pp. 6–10). Guangzhou, China. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCS59553.2023.10455452
Utami, W. T., Mustadi, A., Marsigit, M., & Ibrahim, I. (2021). Hubungan Disposisi Matematis Dan Self-Efficacy Mahasiswa. AKSIOMA: Jurnal Program Studi Pendidikan Matematika, 10(1), 117–124. https://doi.org/10.24127/ajpm.v10i1.3025
Wahyuningrum, E., Bonyah, E., Yumiati, Kartono, & Wijayanti, N. (2024). Exploring the relationship between problem-solving ability and mathematical disposition in 10-11 year ’ s old students using model-eliciting activities. Al-Jabar: Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 15(02), 333–347. https://doi.org/10.24042/ajpm.v15i2.23765
Yount, R. (2018). Research Design and Statistical Analysis in Christian Ministry. Educational Research and Statistics CEST 6300, XXIII(595), 1–9.
Yusnita, I., Sumarmo, U., & Fitriani, N. (2025). Exploratory Data Analysis on Mathematics Learning Difficulties for Junior High School on Solving Story Problems in Terms of Gender. Journal of Innovative Mathematics Learning (JIML), 8(1), 100–112. https://doi.org/https://dx.doi.org/10.22460/jiml.v8i1.p25262
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Hevi Haplatul Mubarokah, Sinta Verawati Dewi, Depi Setialesmana

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Education and Talent Development Center of Indonesia (ETDC Indonesia)
e-mail: kognitif@gmail.com, website : https://etdc-indonesia.com

Kognitif: Jurnal Riset HOTS Pendidikan Matematika dengan Situs: https://etdci.org/journal/kognitif berlisensi Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License









.png)

