Understanding the Role of Think-Pair-Share Strategy in Mathematics Classroom
https://doi.org/10.51574/kognitif.v5i3.3414
Keywords:
Think-Pair-Share, Active Learning, Mathematical Concept Understanding, Cooperative Strategy, Mathematical Communication, Learning MotivationAbstract
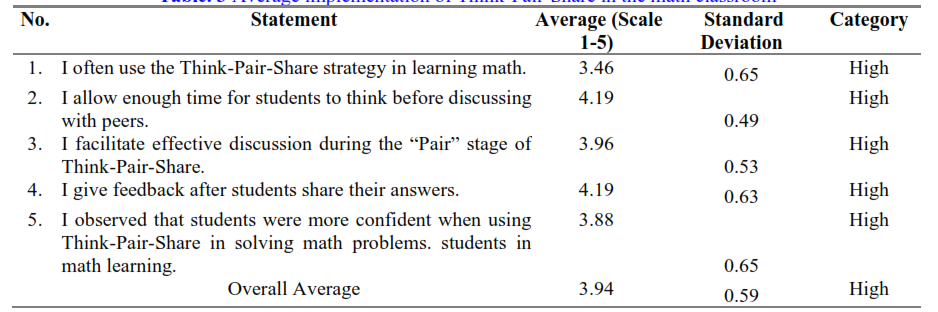
Low student engagement in mathematics learning remains a serious challenge in various schools and universities in Banten Province. Although the Think-Pair-Share (TPS) strategy is recognised as effective in promoting active participation and conceptual understanding, its implementation in the field is uneven and lacks contextual evidence. This study aims to analyse the perceptions of mathematics teachers and lecturers regarding the implementation of TPS, specifically in terms of anticipated benefits, obstacles experienced, and opportunities for classroom implementation. Using a quantitative descriptive approach, data were collected through a survey of 26 respondents who offered to participate in the study. The instrument was a closed questionnaire with five Likert scales with 45 statement points covering nine indicators of TPS implementation. Data were analysed using descriptive statistics, which involved calculating the average score for each indicator and creating a frequency distribution. The results showed that respondents generally had a positive perception of TPS, particularly in fair students’ understanding of mathematical concepts and communication skills. However, the main obstacles involved limited implementation time and diversity in student participation. Some respondents also mentioned the lack of practical training and the difficulty in adapting strategies to the characteristics of the class. Although the sample size is limited, this study makes an initial contribution to understanding the dynamics of TPS implementation in the local context. It is recommended that teacher training focus on the technical aspects of TPS implementation and be accompanied by flexible and context-based guidance to support the effectiveness of cooperative learning in mathematics classes.
Downloads
References
Arlina, A., Hasibuan, R. M., Syahida, N. A., Aqilla, N. P., & Aulaz, I. (2023). Meningkatkan Keterlibatan Siswa di Kelas Menggunakan Model Pembelajaran Think Pair Share. At-Tadris: Journal of Islamic Education, 2(2), 270–281. https://doi.org/10.56672/attadris.v2i2.101
Asria, V. Z. (2019). Improving concept comprehension ability in mathematics by using mathematical model: Think-pair-share approach. 1402(7), 077083. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1402/7/077083
Belleantari, N. (2025). Implementasi Model Pembelajaran Kooperatif Tipe Think Pair Share (TPS) Untuk Meningkatkan Motivasi Belajar Akuntansi Siswa Kelas X Akuntansi. Jurnal Intelektual Indo-MathEdu , 6 (1), 112–119. https://doi.org/10.54373/imeij.v6i1.2452
Deore, M., & Arora, S. (2022). Effective Think-Pair-Share Pedagogical Strategy to Improve Inferential Statistics Concept Understanding. Journal of Engineering Education Transformations, 36(S1), 25–32. https://doi.org/10.16920/jeet/2022/v36is1/22170
Firdaus, H., & Satriawan, R. (2025). Collaborative Learning Strategies in Developing Critical Thinking of Students in Mathematics. The Journal of Academic Science., 2(1). https://doi.org/10.59613/g6stj540
Hetmanenko, L. (2024). The role of interactive learning in mathematics education: fostering student engagement and interest. Multidisciplinary Science Journal, 6, 2024ss0733. https://doi.org/10.31893/multiscience.2024ss0733
Hidayatullah, A., Syamsuri, S., Fathurrohman, M., & Nindiasari, H. (2024). Meta analisis: pengaruh model pembelajaran tps terhadap hasil belajar matematika siswa. Jurnal Lebesgue, 5(1), 591–596. https://doi.org/10.46306/lb.v5i1.535
Johnson, D. W., & Johnson, R. T. (1999). Learning together and alone: Cooperative, competitive, and individualistic learning (5th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn and Bacon
Johnson, D. W., Johnson, R. T., & Holubec, E. J. (1999). Cooperation in the classroom (7th ed.). Edina, MN: Interaction Book Company.
Johnson, D. W., Johnson, R. T., & Holubec, E. J. (2009). Circles of learning: Cooperation in the classroom (7th ed.). Interaction Book Company.
Khairunisa, R. W., & Basuki, B. (2021). Perbandingan Kemampuan Komunikasi Matematis Siswa antara Model Pembelajaran Kooperatif Tipe TPS dan CIRC. Plusminus: Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 1(1), 113–124. https://doi.org/10.31980/plusminus.v1i1.881
Laela, I. N., Nurlatifah, M., Atika, N. Z., Salsabila, R., & Septiana, U. (2024). Penerapan Model Collaborative Learning Untuk Meningkatkan Critical Thinking Skill Pada Siswa Sekolah Dasar. https://doi.org/10.55606/jpbb.v3i1.2710
Main, K. (2020). Cooperative and collaborative learning (pp. 191–206). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003117780-14
Nasir, A. (2018). The implementing of think-pair-share (tps) strategy in teaching speaking skills. 1(1), 8–13. http://sastra.unifa.ac.id/journal/index.php/jes/article/view/7
Nurlaika, F., Sahade, S., & Rijal, A. (2024). The Effect of Cooperative Learning Model Type Think Pair Share (TPS) on Student Learning Outcomes. Golden Ratio of Data in Summary, 4(2), 641–653. https://doi.org/10.52970/grdis.v4i2.648
Rhee, J., & Shin, H. W. (2024). Recognition of Cooperative Learning through Reflection Journal. 36(4), 55–67. https://doi.org/10.19031/jkheea.2024.12.36.4.55
Sampsel, A. (2013). Finding the Effects of Think-Pair-Share on Student Confidence and Participation. https://scholarworks.bgsu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1029&context=honorsprojects
Siswanto, D. H., & Susetyawati, M. M. E. (2024). Comparison of the Effectiveness of Cooperative Learning Models TPS and GI on Students’ Mathematical Concept Understanding Ability. https://doi.org/10.55927/ijsmr.v2i7.10034
Sugiyono. (2017). Metode penelitian pendidikan: Pendekatan kuantitatif, kualitatif, dan R&D. Alfabeta.
Vale, I., & Barbosa, A. M. F. de C. (2023). Active learning strategies for an effective mathematics teaching and learning. European Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 11(3), 573–588. https://doi.org/10.30935/scimath/13135
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Amalia Ramadhani, Mujadilah Putri Karida , Wahyunengsih

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Education and Talent Development Center of Indonesia (ETDC Indonesia)
e-mail: kognitif@gmail.com, website : https://etdc-indonesia.com

Kognitif: Jurnal Riset HOTS Pendidikan Matematika dengan Situs: https://etdci.org/journal/kognitif berlisensi Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License









.png)

