Implementation of the Numbered Heads Together Model Based on Problem Based Learning on Students’ Interest and Understanding of Mathematical Concepts
https://doi.org/10.51574/kognitif.v5i4.3312
Keywords:
Numbered Heads Together (NHT) , Problem Based Learning (PBL), Learning Interest, Conceptual Understanding of MathematicsAbstract
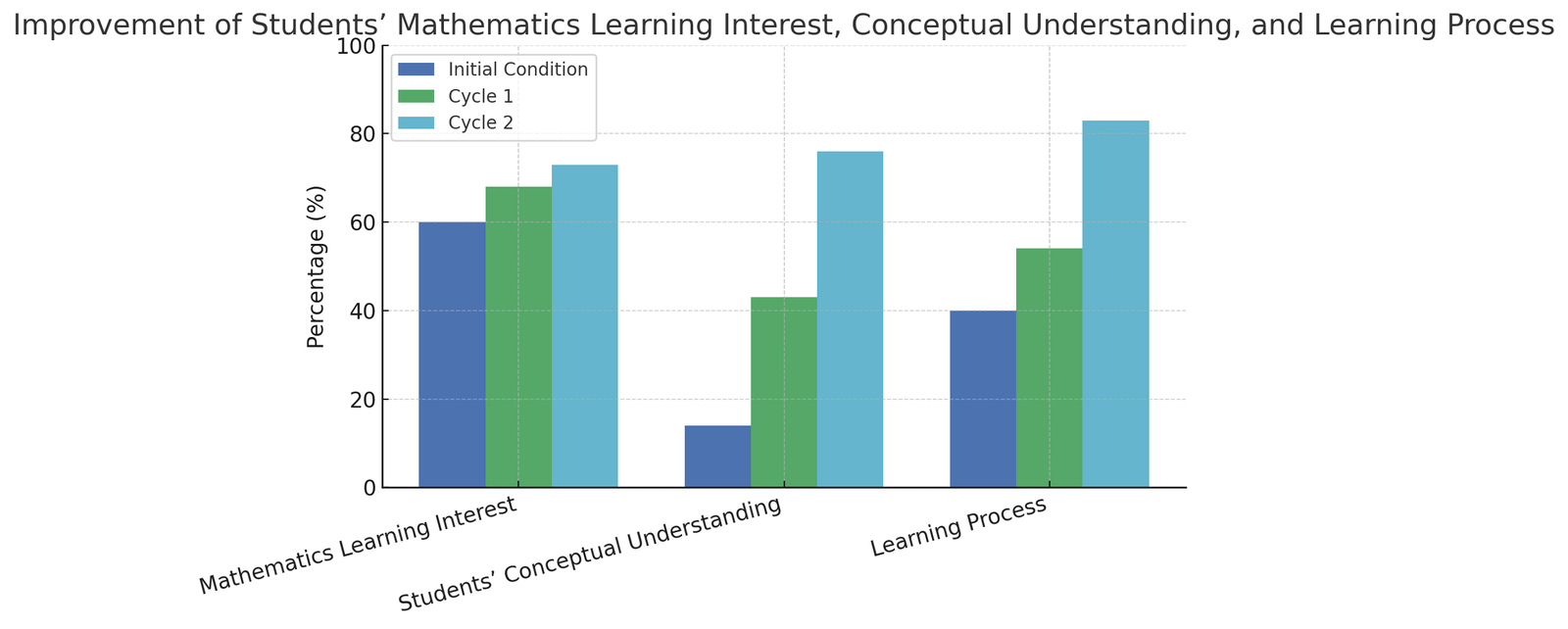
Mathematics is often perceived by students as a difficult and uninteresting subject, highlighting the need for a learning model that not only fosters interest but also strengthens conceptual understanding. Previous studies have shown a gap in the optimal integration of the cooperative Numbered Heads Together (NHT) model with the Problem Based Learning (PBL) approach, even though both have the potential to promote active engagement and stimulate critical thinking. This study aims to examine the effectiveness of implementing the PBL-based NHT model in improving students’ interest and conceptual understanding of mathematics among tenth-grade students at MA Zainul Hasan Genggong. The research was conducted through Classroom Action Research, combining quantitative data (tests and questionnaires) and qualitative data (observations and interviews). The participants consisted of 21 students. The instruments included a learning interest questionnaire, multiple-choice tests to assess conceptual understanding, observation sheets, and interview guidelines. The results indicate an increase in the average learning interest score from 61% (moderate category) to 73% (high category), and an improvement in conceptual understanding from an average of 42.86% in Cycle I to 82.61% in Cycle II. The qualitative data supported these findings, showing students’ more active involvement in discussions and problem-solving activities. Therefore, the integration of the NHT–PBL model proved effective in enhancing students’ interest and conceptual understanding. These findings recommend strengthening problem-based cooperative learning designs by considering aspects such as time allocation, topic selection, and students’ ability heterogeneity.
Downloads
References
Adu-Gyamfi, K., Bossé, M. J., Preston, R. V, & Williams, D. (2020). The Problem of Simplification in School Mathematics. Mathematics Teacher: Learning and Teaching PK–12, 113(2), 160–163. https://doi.org/10.5951/MTLT.2019.0072
Alifani, W., Hakim, A., Sofia, B. F. D., & Al Idrus, S. W. (2022). Pengembangan Modul Praktikum Kimia Mandiri Berbasis Kimia Komputasi Pada Pokok Bahasan Sistem Periodik Unsur. Jurnal Ilmiah Profesi Pendidikan, 7(3b). https://doi.org/10.29303/jipp.v7i3b.814
Boaler, J., Brown, K., LaMar, T., Leshin, M., & Selbach-Allen, M. (2022). Infusing Mindset through Mathematical Problem Solving and Collaboration: Studying the Impact of a Short College Intervention. Education Sciences, 12(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12100694
Diana, L. M., Arif, M., Stefany, E. M., & Aini, N. (2023). Model Pembelajaran Numbered Head Together Untuk Meningkatkan Hasil Belajar Siswa. Jurnal Ilmiah Edutic: Pendidikan Dan Informatika, 9(2), 201–211. https://doi.org/10.21107/edutic.v9i2.20224
Hung, W., & Amida, A. (2020). Problem-Based Learning in College Science. In [Book Title jika ada] (pp. 325–339). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-33600-4_21
Kant, D., & Sarikaya, D. (2021). Mathematizing as a virtuous practice: different narratives and their consequences for mathematics education and society. Synthese, 199(1–2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11229-020-02939-y
Larasati, I. (2020). Evaluasi Penggunaan Website Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta Dengan Menggunakan Metode Usability Testing. Computatio : Journal of Computer Science and Information Systems, 4(1). https://doi.org/10.24912/computatio.v4i1.6689
Mariwati, K., & Saija, L. M. (2024). The Effect of Junior High School Students Extrinsic Motivation towards Mathematical Understanding Ability. Jurnal Padegogik, 7(2), 97–103. https://doi.org/10.35974/jpd.v7i2.3433
Maulana, A. (2022). Analisis Validtas, Reliabilitas, dan Kelayakan Instrumen Penilaian Rasa Percaya Diri Siswa. Jurnal Kualita Pendidikan, 3(3). https://doi.org/10.51651/jkp.v3i3.331
Md Zain, A. N., & Rahayu, N. (2023). Systematic Literature Review: Factors Causing Low Students’ Interest in Learning Mathematics. Logaritma, 11(1), 105–118. https://doi.org/10.24952/logaritma.v11i1.8333
Miles, M. B., & Huberman, A. M. (1994). Miles and Huberman 1994.pdf. In Qualitative Data Analysis: An Expanded Sourcebook.
Munna, A. S., & Kalam, M. A. (2021). Impact of Active Learning Strategy on the Student Engagement. GNOSI: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Human Theory and Praxis, 4(2).
Nemakhavhani, R. B. (2024). Enhancing Student Engagement Through Problem-Based Learning: A Case of the Built Environment. https://doi.org/10.34190/icer.1.1.3053
Odeh, O. (2021). Pengaruh Penggunaan Model Problem Based Learning Terhadap Minat Belajar Siswa Kelas VII-B SMPN 1 Karangjaya. J-KIP (Jurnal Keguruan Dan Ilmu Pendidikan), 2(2). https://doi.org/10.25157/j-kip.v2i2.5204
Rahmawati, N., Otaiwi, Z., Nakkhasen, W., & Thãnh, N. P. (2023). Increasing Mathematics Learning Activities Through Numbered Heads Together (NHT) Cooperative Learning Models In Students. Interval: Indonesian Journal of Mathematical Education, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.37251/ijome.v1i1.608
Schmidt, W. H., Houang, R. T., Sullivan, W. F., & Cogan, L. S. (2022). When practice meets policy in mathematics education: A 19 country/jurisdiction case study. In OECD Education Working Papers (Vol. 268). OECD Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1787/07d0eb7d-en
Tolqunovna, T. X., & Leonodovna, M. N. (2024). Understanding the pedagogical basis of students’ interest in professions: a comprehensive analysis. International Journal of Advances in Scientific Research. https://doi.org/10.37547/ijasr-04-03-23
Walle, J. A. V. de, Karp, K. S., & Bay-Williams, J. M. (2020). Elementary and Middle School Mathematics: Teaching Developmentally (Book). In Teaching Children Mathematics (Vol. 10, Issue 5).
Warsah, I., Morganna, R., Uyun, M., Hamengkubuwono, H., & Afandi, M. (2021). The Impact of Collaborative Learning on Learners’ Critical Thinking Skills. International Journal of Instruction, 14(2). https://doi.org/10.29333/iji.2021.14225a
Yu, L., & Zin, Z. M. (2023). The critical thinking-oriented adaptations of problem-based learning models: a systematic review. In Frontiers in Education (Vol. 8). https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2023.1139987
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Anisa Qarinatul Izza, Khofifah Indah Mubarokah, Loviga Denny Pratama

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Education and Talent Development Center of Indonesia (ETDC Indonesia)
e-mail: kognitif@gmail.com, website : https://etdc-indonesia.com

Kognitif: Jurnal Riset HOTS Pendidikan Matematika dengan Situs: https://etdci.org/journal/kognitif berlisensi Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License









.png)

