Enhancing Students’ Mathematics Learning Outcomes through Problem-Based Learning
https://doi.org/10.51574/kognitif.v5i4.2975
Keywords:
Problem-Based Learning (PBL), Mathematics Learning Outcomes, Relations and Functions, Student EngagementAbstract
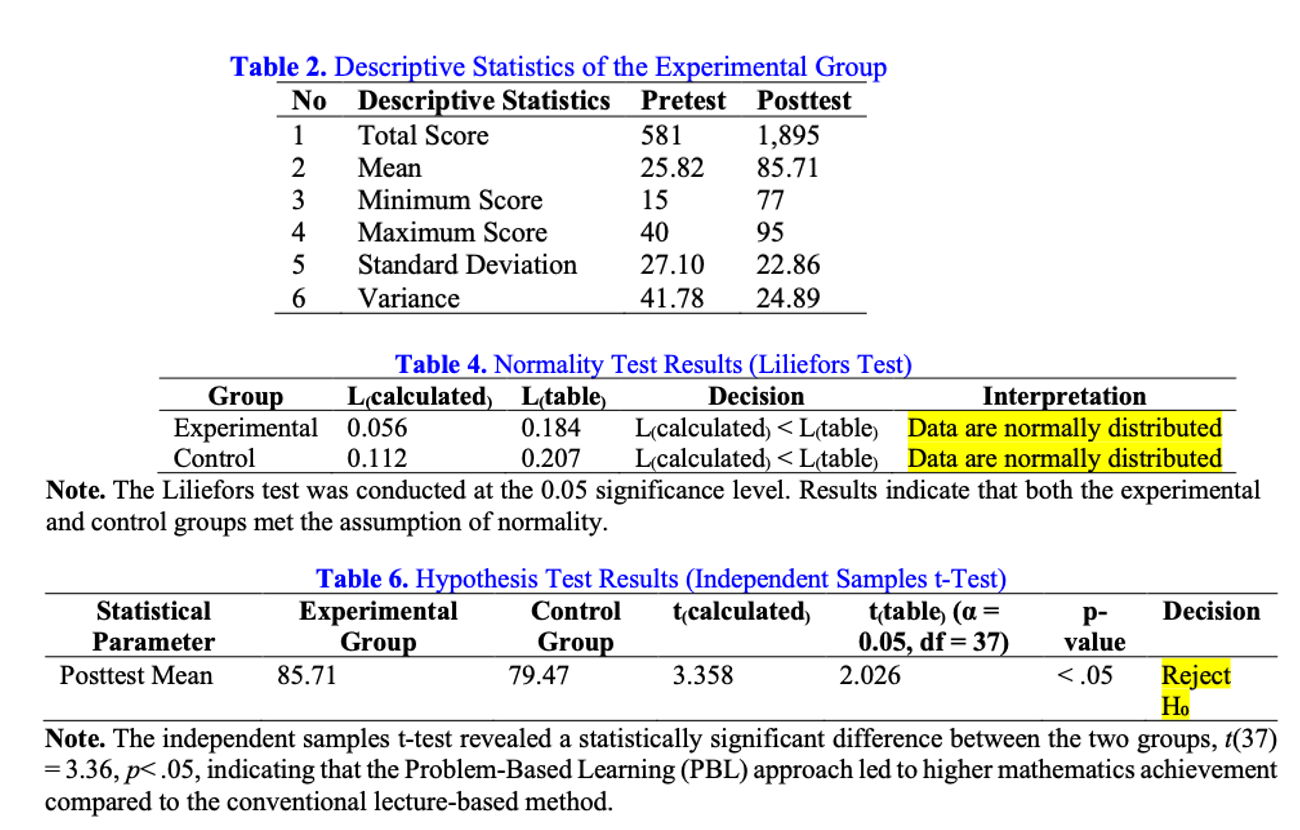
Low levels of student engagement and learning motivation have led to limited critical thinking skills, which in turn have affected students’ learning outcomes that remain below the Minimum Mastery Criteria (MMC). This study aims to determine whether students who received instruction through the Problem-Based Learning (PBL) model achieved higher mathematics learning outcomes than those taught using the conventional (lecture-based) model on the topic of Relations and Functions. This research employed a quasi-experimental method with a pretest–posttest control group design. Population consisted of eighth-grade students from SMP Negeri 3 Tondano, while the samples were class VIII-A (22 students) as the experimental group and class VIII-B (17 students) as the control group. The research instrument comprised written essay tests administered as pretests and posttests in both groups. Data were analyzed using inferential statistical procedures. Data were first tested for normality using the Liliefors test, followed by a homogeneity test (F-test). After both assumptions were met, an independent samples t-test (two-tailed) was performed to test the hypothesis. The results showed a statistically significant difference in mathematics learning outcomes between students who learned through the PBL model and those taught using the conventional lecture-based method. Therefore, it can be concluded that the implementation of the PBL model effectively enhances students’ mathematics learning outcomes on the topic of Relations and Functions, providing evidence that active, problem-oriented instruction can improve students’ conceptual understanding and achievement in mathematics.
Downloads
References
Achmetli, K., Schukajlow, S., & Rakoczy, K. (2019). Multiple Solutions for Real-World Problems, Experience of Competence and Students’ Procedural and Conceptual Knowledge. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 17(8), 1605–1625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-018-9936-5
Amador, J. M., Glassmeyer, D., & Brakoniecki, A. (2024). Teachers’ noticing of proportional reasoning. Journal of Mathematics Teacher Education, January. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10857-024-09625-7
Aries, A. (2022). Pengaruh Model Pembelajaran Problem Based Learning (PBL) Terhadap Hasil Belajar Matematika Pada Siswa Kelas VII Di SMP Sultan Agung Surabaya. Postulat : Jurnal Inovasi Pendidikan Matematika, 3(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.30587/postulat.v3i1.4312
Callingham, R., & Siemon, D. (2021). Connecting multiplicative thinking and mathematical reasoning in the middle years. Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 61(December 2020), 100837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmathb.2020.100837
Carlson, M. P., & Thompson, P. W. (2017). Variation , covariation , and functions : Foundational ways of thinking mathematically. In Compendium for research in mathematics education (pp. 421–456) (Issue January).
Degrande, T., Verschaffel, L., & Van Dooren, W. (2017). Spontaneous Focusing on Quantitative Relations: Towards a Characterization. Mathematical Thinking and Learning, 19(4), 260–275. https://doi.org/10.1080/10986065.2017.1365223
Eriksson, H., & Sumpter, L. (2021). Algebraic and fractional thinking in collective mathematical reasoning. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 473–491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-021-10044-1
Fuentealba, C., Sánchez-Matamoros, G., Badillo, E., & Trigueros, M. (2017). Thematization of derivative schema in university students: nuances in constructing relations between a function’s successive derivatives. International Journal of Mathematical Education in Science and Technology, 48(3), 374–392. https://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2016.1248508
Habsyi, R., R. M. Saleh, R., & Isman M. Nur. (2022). Pengembangan E-LKPD Berbasis Guided Dicovery Learning untuk Meningkatkan Kemampuan Berpikir Kritis Siswa. Kognitif: Jurnal Riset HOTS Pendidikan Matematika, 2(1), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.51574/kognitif.v2i1.385
Hackenberg, A. J., Aydeniz, F., & Jones, R. (2021). Middle school students ’ construction of quantitative unknowns ⋆. Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 61(December 2020), 100832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmathb.2020.100832
Hollebrands, K. F., & Lee, H. S. (2020). Effective design of massive open online courses for mathematics teachers to support their professional learning. ZDM - Mathematics Education, 52(5), 859–875. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-020-01142-0
Jones, S. R. (2017). An exploratory study on student understandings of derivatives in real-world, non-kinematics contexts. Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 45, 95–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmathb.2016.11.002
Jones, S. R., & Kuster, G. E. (2021). Examining students ’ variational reasoning in differential equations. Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 64(January), 100899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmathb.2021.100899
Kim, Y. R., Park, M. S., Moore, T. J., & Varma, S. (2013). Multiple levels of metacognition and their elicitation through complex problem-solving tasks. Journal of Mathematical Behavior, 32(3), 377–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmathb.2013.04.002
Kotto, M. A., Babys, U., & Gella, N. J. M. (2022). Meningkatkan Kemampuan Penalaran Matematika Siswa Melalui Model PBL (Problem Based Learning). Jurnal Sains Dan Edukasi Sains, 5(1), 24–27. https://doi.org/10.24246/juses.v5i1p24-27
Lee, Y., Capraro, R. M., & Bicer, A. (2019). Affective Mathematics Engagement: a Comparison of STEM PBL Versus Non-STEM PBL Instruction. Canadian Journal of Science, Mathematics and Technology Education, 19(3), 270–289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42330-019-00050-0
Makitalentu, C., Manurung, O., & Regar, V. E. (2023). Penerapan Model Problem Based Learning Pada Pembelajaran Relasi Dan Fungsi. Jurnal Sosial Humaniora Sigli, 6(2), 767–770.
Mohamed Abdul-Rahmana, M. A. M. (2020). Effectiveness of learner control and program control strategies in developing mathematical thinking for slow learners in mathematics. International Journal of Innovation, Creativity and Change, 12(12).
Nolaputra, A. P., Wardono, & Supriyono. (2018). Analisis Kemampuan Literasi Matematika pada Pembelajaran PBL Pendekatan RME Berbantuan Schoology Siswa SMP. Prisma, Prosiding Seminar Nasional Matematika, 1.
Nur, M. A. (2024). Meta Analisis Pengaruh Model Pembelajaran Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL) terhadap Hasil Belajar Matematika Siswa Sekolah Dasar. Kognitif: Jurnal Riset HOTS Pendidikan Matematika, 4(May), 151–160. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.51574/kognitif.v4i1.1409
OECD. (2018). Programme for International Students Assesment (PISA) Result From PISA 2018.
Ostermann, A., Leuders, T., & Nückles, M. (2018). Improving the judgment of task difficulties: prospective teachers’ diagnostic competence in the area of functions and graphs. Journal of Mathematics Teacher Education, 21(6), 579–605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10857-017-9369-z
Putranto, S., & Marsigit, M. (2018). Is it Effective using Peer Tutoring with Realistic Mathematics Education Approach to Improve Slow Learners’ Mathematics Attitudes? International Journal on Emerging Mathematics Education, 2(2). https://doi.org/10.12928/ijeme.v2i2.10487
Rahayuningsih, S., Nurasarawati, N., & Nurhusain, M. (2022). Komparasi Efektivitas Model Pembelajaran Project Based Learning (PjBL) dan Konvensional: Studi Pada Siswa Menengah Pertama. Kognitif: Jurnal Riset HOTS Pendidikan Matematika, 2(2), 118–129.
Son, J. W., & Lee, M. Y. (2021). Exploring the Relationship Between Preservice Teachers’ Conceptions of Problem Solving and Their Problem-Solving Performances. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 19(1), 129–150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-019-10045-w
Tallman, M. A., & Frank, K. M. (2020). Angle measure, quantitative reasoning, and instructional coherence: an examination of the role of mathematical ways of thinking as a component of teachers’ knowledge base. Journal of Mathematics Teacher Education, 23(1), 69–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10857-018-9409-3
Tran, T., Nguyen, T. T. T., Le, T. T. T., & Phan, T. A. (2020). Slow learners in mathematics classes: the experience of Vietnamese primary education. Education 3-13, 48(5). https://doi.org/10.1080/03004279.2019.1633375
Viirman, O. (2015). Explanation , motivation and question posing routines in university mathematics teachers ’ pedagogical discourse : a commognitive analysis. International Journal of Education in Science and Techology, 48(8), 1165–1181. https://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2015.1034206
Wilkie, K. J. (2020). Investigating Students’ Attention to Covariation Features of their Constructed Graphs in a Figural Pattern Generalisation Context. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 18(2), 315–336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-019-09955-6
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Agnes Pesta Kristiani Pardede, Philotheus E.A Tuerah, Ermita, Galih Albarra Shidiq

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Education and Talent Development Center of Indonesia (ETDC Indonesia)
e-mail: kognitif@gmail.com, website : https://etdc-indonesia.com

Kognitif: Jurnal Riset HOTS Pendidikan Matematika dengan Situs: https://etdci.org/journal/kognitif berlisensi Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License









.png)

