Analysis of Guru Penggerak Program: Teacher Satisfaction and Method Implementation Across Different Demographics
https://doi.org/10.51574/kognitif.v5i1.2815
Keywords:
Guru Penggerak, Teacher Satisfaction, Demographics, Mathematics Education, TeacherAbstract
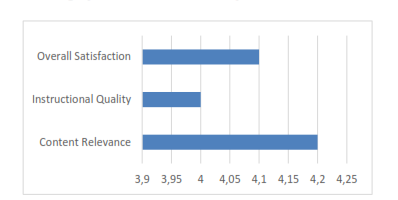
This study evaluates the impact of the "Guru Penggerak" program on teaching practices and participant satisfaction, focusing on educators from 36 cities across Indonesia. The program “Guru Penggerak”, initiated by the Indonesian Ministry of Education, empowers teachers to become leaders in educational transformation. It enhances pedagogical skills, leadership abilities, and the integration of local wisdom with global knowledge to develop reflective and innovative educators. This research examines the relationship between satisfaction levels and demographic factors—age, gender, and teaching experience—as well as the frequency of implementing learned methods. Participants (N = 119), predominantly female and experienced educators, rated program aspects, including content relevance, instructional quality, and overall satisfaction, using a Likert scale. Mean ratings ranged from 4.0 to 4.2, indicating a positive reception. Pearson correlation analysis assessed relationships between demographic factors, satisfaction, and implementation frequency. Results showed minimal correlations (age: r = -0.115, gender: r = -0.059, teaching experience: r = -0.006) for satisfaction and weak correlations (age: r = 0.066, gender: r = -0.062, teaching experience: r = 0.127) for implementation frequency, suggesting demographic factors had little influence. Findings indicate the program is well-received across diverse demographics, reinforcing its broad effectiveness. Future research should incorporate qualitative methods to explore additional factors, such as school infrastructure and individual teaching styles, that may influence satisfaction and practical application. Identifying these factors will contribute to optimizing teacher development programs and enhancing their impact on Indonesia’s education system.
Downloads
References
Bell, J., Wilcoxen, C., & Steiner, A. (2022). Mentoring and coaching through induction to develop reflective practices in beginning teachers. The New Educator, 18(4), 281–305.
Chew, S. L., & Cerbin, W. J. (2021). The cognitive challenges of effective teaching. The Journal of Economic Education, 52(1), 17–40.
Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2017). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. Sage publications.
Darling-Hammond, L., Hyler, M. E., & Gardner, M. (2017). Effective teacher professional development. Learning Policy Institute.
Dvir, N., & Schatz-Oppenheimer, O. (2020). Novice teachers in a changing reality. European Journal of Teacher Education, 43(4), 639–656.
Gheyssens, E., Coubergs, C., Griful-Freixenet, J., Engels, N., & Struyven, K. (2022). Differentiated instruction: the diversity of teachers’ philosophy and praxis to adapt teaching to students’ interests, readiness and learning profiles. International Journal of Inclusive Education, 26(14), 1383–1400.
Haig, Y., & Barratt-Pugh, C. (2015). Indonesian teachers’ implementation of new curriculum initiatives in relation to teaching writing in lower primary school.
Harapan, R. (2017). Pengaruh kepemimpinan kepala sekolah terhadap kinerja guru di MAN 2 Padangsidimpuan. Al-Muaddib: Jurnal Ilmu-Ilmu Sosial Dan Keislaman, 1(1).
Herrick, J. (2023). Re-Engaging Veteran Teachers in Professional Development: Fostering Environment and Voice. https://search.proquest.com/openview/e3d39927d988628cd4ffb745cfed7f5c/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=18750&diss=y
Hogan, J. P., & White, P. (2021). A self-study exploration of early career teacher burnout and the adaptive strategies of experienced teachers. Australian Journal of Teacher Education (Online), 46(5), 18–39.
Jawas, U. (2014). Instructional leadership in Indonesian school reform: local perceptions and practices. https://researchprofiles.canberra.edu.au/files/33684388/file
Karlberg, M., & Bezzina, C. (2022). The professional development needs of beginning and experienced teachers in four municipalities in Sweden. Professional Development in Education, 48(4), 624–641.
Kementerian Pendidikan, K. R. dan T. (2024a). Detil Program Guru Penggerak. https://sekolah.penggerak.kemdikbud.go.id/gurupenggerak/detil-program/
Kementerian Pendidikan, K. R. dan T. (2024b). Peraturan Mendikbudristek No. 12 Tahun 2024 tentang Kurikulum pada PAUD, Jenjang Pendidikan Dasar, dan Jenjang Pendidikan Menengah. https://kurikulum.kemdikbud.go.id/file/1720050615_manage_file.pdf
Kraft, M. A., Blazar, D., & Hogan, D. (2018). The effect of teacher coaching on instruction and achievement: A meta-analysis of the causal evidence. Review of Educational Research, 88(4), 547–588.
Kurnianingsih, E. (2018). Peran kepala sekolah dalam meningkatkan kompetensi guru. Indonesian Journal of Education Management & Administration Review, 1(1), 11–18.
Rauschenberger, E. (2020). From teach for America to teach first: The initial expansion overseas. In Examining Teach for All (pp. 13–35). Routledge.
Sims, S., & Fletcher-Wood, H. (2021). Identifying the characteristics of effective teacher professional development: a critical review. School Effectiveness and School Improvement, 32(1), 47–63.
Svenja, V., David, K., Eckhard, K., & Sonja, B. (2012). TALIS teaching practices and pedagogical Innovations evidence from TALIS: Evidence from TALIS. OECD publishing.
Widayati, A., MacCallum, J., & Woods-McConney, A. (2021). Teachers’ perceptions of continuing professional development: a study of vocational high school teachers in Indonesia. Teacher Development, 25(5), 604–621.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Valeria Yekti Kwasaning Gusti , Thesa Kandaga, Suci Nurhayati, Erna Risnawati

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Education and Talent Development Center of Indonesia (ETDC Indonesia)
e-mail: kognitif@gmail.com, website : https://etdc-indonesia.com

Kognitif: Jurnal Riset HOTS Pendidikan Matematika dengan Situs: https://etdci.org/journal/kognitif berlisensi Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License









.png)

