Enhancing Mathematics Education through Lesson Study Based on Didactical Suitability Criteria: Evidence from Undergraduate Courses
Keywords:
Lesson Study, Didactical Suitability Criteria, Mathematics Education, Undergraduate Students, Innovative LearningAbstract
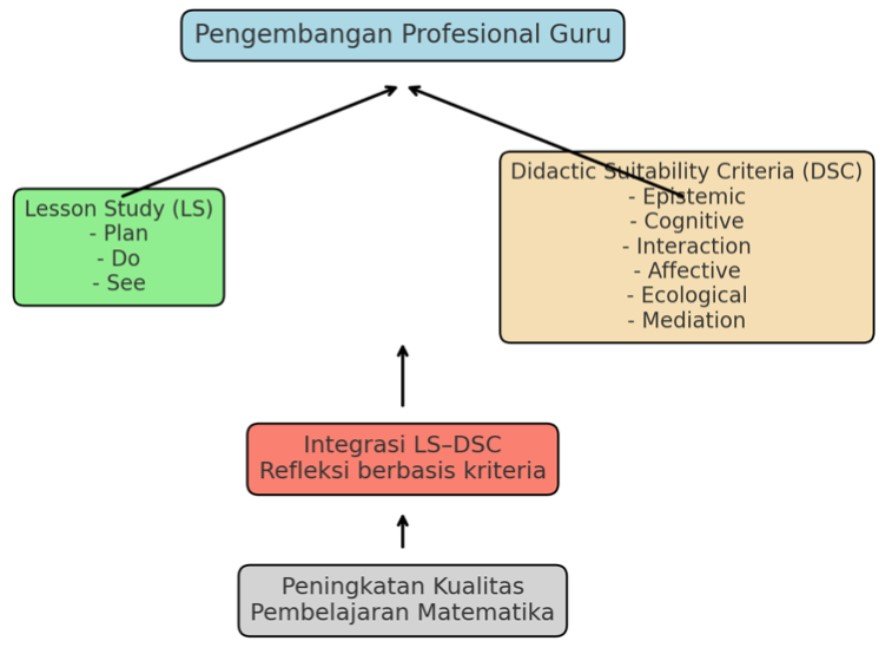
Innovation in mathematics education is essential to improve the quality of university learning, which should not only emphasize cognitive achievement but also broader didactical dimensions. This study aims to implement Lesson Study based on the Didactical Suitability Criteria (LS-DSC) in mathematics education lectures for undergraduate students at Universitas Islam Ahmad Dahlan, and to evaluate its impact on six dimensions of didactical suitability: epistemic, cognitive, interactional, affective, mediational, and ecological. This research employed a descriptive qualitative approach with a lesson study design consisting of three main stages: plan–do–see. The participants included lecturers as facilitators and students as active learners. Data were collected through classroom observation, analysis of students’ worksheets, reflective notes, and documentation of learning activities. The data were then analyzed using reduction, presentation, and verification techniques.
The findings reveal that LS-DSC effectively enhanced learning quality across all six dimensions. The most significant improvements were observed in the cognitive, affective, and interactional dimensions, which strengthened student participation and learning motivation. The epistemic and mediational dimensions demonstrated consistency in supporting conceptual understanding and the use of appropriate learning resources, while the ecological dimension highlighted the relevance of learning to students’ real-life contexts. These results align with constructivist theory and previous studies that emphasize the effectiveness of lesson study in improving mathematics teaching practices. Therefore, LS-DSC can be considered an innovative model that not only improves learning quality but also fosters lecturers’ professional development and enriches students’ learning experiences.
References
Brousseau, G. (1997). Theory of didactical situations in mathematics: Didactique des mathématiques, 1970–1990. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Cobb, P., & Yackel, E. (1996). Constructivist, emergent, and sociocultural perspectives in the context of developmental research. Educational Psychologist, 31(3–4), 175–190. https://doi.org/10.1080/00461520.1996.9653265
Deci, E. L., & Ryan, R. M. (2000). The “what” and “why” of goal pursuits: Human needs and the self-determination of behavior. Psychological Inquiry, 11(4), 227–268. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15327965PLI1104_01
Fernandez, C. (2002). Learning from Japanese approaches to professional development: The case of lesson study. Journal of Teacher Education, 53(5), 393–405. https://doi.org/10.1177/002248702237394
Fernandez, C., & Yoshida, M. (2004). Lesson study: A Japanese approach to improving mathematics teaching and learning. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Fujii, T. (2016). Designing and adapting tasks in lesson planning: A critical process of lesson study. ZDM Mathematics Education, 48(4), 411–423. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-016-0780-3
Godino, J. D., & Font, V. (2010). The theory of didactic suitability: Criteria for analysing the adequacy of mathematical instruction. In B. Sriraman & L. English (Eds.), Theories of mathematics education: Seeking new frontiers (pp. 111–133). Berlin, Germany: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-00742-2_12
Godino, J. D., Batanero, C., & Font, V. (2007). The onto-semiotic approach to research in mathematics education. ZDM Mathematics Education, 39(1–2), 127–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-006-0004-1
Isoda, M. (2015). Lesson study: Problem solving approaches in mathematics education as a Japanese experience. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 174, 1291–1298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.01.747
Kaharuddin, A., García, J. G., Magfirah, I., & Yulismayanti, Y. (2025). Validating a TPCK-S Instrument for Hologram-Based Mathematics Teaching. Indonesian Journal on Learning and Advanced Education (IJOLAE).
Lewis, C. (2002). Lesson study: A handbook of teacher-led instructional change. Philadelphia, PA: Research for Better Schools.
Pino-Fan, L. R., Godino, J. D., & Font, V. (2018). Assessing key epistemic features of mathematics classroom practices: A focus on the epistemic suitability. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 97(1), 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10649-017-9797-6
Sari, N., Kaharuddin, A., Zulfikar, M., Elvierayani, R. R., Rinawati, A., Kuspiyah, H. R., ... & Ramadan, N. S. (2025). Strategi Pembelajaran Mendalam. Andi Kaharuddin.
Sweller, J. (1994). Cognitive load theory, learning difficulty, and instructional design. Learning and Instruction, 4(4), 295–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/0959-4752(94)90003-5
Toh, T. L. (2020). Motivation and affect in mathematics learning: The role of instructional strategies. Journal of Mathematics Education, 13(2), 45–60.
Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind in society: The development of higher psychological processes. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Yerushalmy, M. (2014). Mobile technologies in mathematics classrooms: Potential and challenges. International Journal of Mobile and Blended Learning, 6(2), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.4018/ijmbl.2014040101