Implementation of Fun Learning Methods to Improve Mathematics Learning Outcomes of Grade III Students
Keywords:
Fun learning, Learning outcomes, MathematicsAbstract
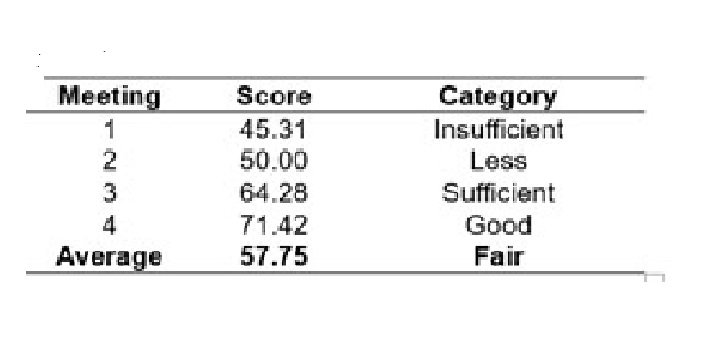
This study was motivated by the low mathematics learning outcomes of third-grade students at State Elementary School 5 Sesean, where 70% of students had not achieved the minimum passing grade. This condition was influenced by the dominance of the lecture method, which made students less active and less motivated. This study aims to describe the improvement in mathematics learning outcomes through the application of the fun learning method. The type of research used is Classroom Action Research (CAR) with two cycles, involving 20 students as research subjects. Data were collected through observation, interviews, documentation, and written tests, then analyzed qualitatively and quantitatively. The indicators of success were determined by the implementation of the method at a minimum of 80% and the completion of learning outcomes by at least 80% of students. The results showed a significant increase in teacher activity, student activity, and learning outcomes. In cycle I, the average student score was 59.16 with a completion rate of 50%, while in cycle II it increased to 82.25 with a completion rate of 100%. Teacher activity reached an average of 88.67% (good category) and student activity 84.25% (good category). These findings indicate that the fun learning method is effective in increasing student motivation, engagement, and academic achievement in mathematics learning. Thus, fun learning can be used as an alternative learning method to improve the quality of learning outcomes in elementary schools.
References
Bruner, J. S. (1966). Toward a theory of instruction. Harvard University Press.
Bukit, S., Marcela, E. D., & Ernawati. (2023). Teacher’s Strategy to Create Fun Learning in Elementary School. Journal Corner of Education, Linguistics, and Literature, 2(3), 244–249. https://doi.org/10.54012/jcell.v2i3.129
Deci, E. L., & Ryan, R. M. (2000). The “what” and “why” of goal pursuits: Human needs and the self-determination of behavior. Psychological Inquiry, 11(4), 227–268. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15327965PLI1104_01
Fitzgerald, S. L., & Fitzgerald, C. (2020). Make Learning Fun. 8111–8119. https://doi.org/10.21125/edulearn.2020.2026
Gagné, R. M. (1985). The conditions of learning and theory of instruction (4th ed.). Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
Helaluddin, Rante, S. V. N., & Tulak, H. (2020). Penelitian & Pengembangan: Sebuah Tinjauan Teori dan Praktik dalam Bidang Pendidikan." Media Madani (2020). Media Madani.
Kaharuddin, A., Tulak, T., Magfirah, I., & Ode, R. (2021). Mengapa Kita Membutuhkan Teknologi Dalam Pendidikan? Jurnal Keguruan Dan Ilmu Pendidikan, 10(1), 57–61. https://doi.org/10.47178/jkip.v10i1.1279
Kaharuddin, A., Arsyad, N., & Asdar, M. P. (2023). Media Hologram 3D dalam Pembelajaran Geometri untuk meningkatkan keterampilan proses sains. Pustaka Learning.
Kaharuddin, A., García, J. G., Magfirah, I., & Yulismayanti, Y. (2025). Validating a TPCK-S Instrument for Hologram-Based Mathematics Teaching. Indonesian Journal on Learning and Advanced Education (IJOLAE). Kaharuddin, S. P., Kahar, M. J., Ernawati, S. P., Ismiyati, N., Umar, S. P., Murniati, S. P., ... & Susilo, G. (2025). MENGUASAI RISET PENDIDIKAN: Implementasi Best Practice dalam Metodologi Dasar. CV. EUREKA MEDIA AKSARA.
Mokhtar, N., Xuan, L. Z., Lokman, H. F., & Mat, N. H. C. (2023). Theory, Literature Review, and Fun Learning Method Effectiveness in Teaching and Learning. International Journal of Social Science and Education Research Studies, 3(8), 1738–1744. https://doi.org/10.55677/ijssers/V03I8Y2023-30
Mufidah, Lailatul, & Sa’diyah, N. (2020). Penerapan Fun Learning dalam Pembelajaran di Sekolah Dasar. Jurnal Ilmiah Pendidikan Guru Sekolah Dasar, 5(1), 33–42.
Nurmanov, A. T., Ugli, Z. J. G., Khurramovna, S. S., Zebiniso, K., Sevara, P., & Ugli, Z. K. G. (2024). Investigating increasing the level of learning and making students interested in mathematics. Cadernos De Educação Tecnologia E Sociedade, 17(4), 181–189. https://doi.org/10.14571/brajets.v17.nse4.181-189
Piaget, J. (1972). The psychology of the child. Basic Books.
Sampelolo, R., Abdullah, M., Tulak, T., Palayukan, H., Langi, E. L., Tulak, H., Pakiding, A., Pratama, M. P., Tangkearung, S. S., & Duma, S. Y. (2024). Buku Pembelajaran Aktif: Teori dan Aplikasi. Kementerian Hukum dan Hak Asasi Manusia Republik Indonesia.
Sugiyono. (2020). Metode Penelitian Pendidikan: Pendekatan Kuantitatif, Kualitatif, dan R&D. Alfabeta.
Syahrul, S. (2019). Penerapan metode fun learning untuk meningkatkan hasil belajar Bahasa Indonesia siswa SMP Negeri 1 Tompobulu. Jurnal Pendidikan dan Pembelajaran, 6(3), 211–220. https://doi.org/10.24252/jpp.v6i3.8134
Tiarawati, U. H. (2024). Utilizing Snakes And Ladders Media In Learning Mathematic Elementary School Students. Sukartono, 10(2), 296–306. https://doi.org/10.31949/jcp.v10i2.8858
Tulak, T., & Tangkearung, S. S. (2021). Analisis Kemampuan Berpikir Tingkat Tinggi Siswa Pada Mata Pelajaran Matematika. Prosiding Universitas Kristen Indonesia Toraja, 1, 97–106.
Tulak, T., Tangkearung, S. S., Tulak, H., & Paseno, E. W. (2023). Application of Meaningful Learning Model To Improve Student’s Learning Outcomes. 664–675. https://doi.org/10.2991/978-2-38476-108-1_66
Yang, X., & Kaiser, G. (2022). The impact of mathematics teachers’ professional competence on instructional quality and students’ mathematics learning outcomes. Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences, 48, 101225.