Intellectual Security and Artificial Intelligence: Managing the Balance Between Positivity and Negativity
https://doi.org/10.51574/ijrer.v4i4.3194
Keywords:
Artificial Intelligence, Decision-Making, Intellectual Security, Knowledge, Negativity and PositivityAbstract
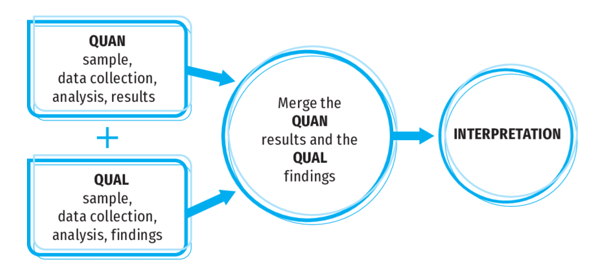
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly reshaping how individuals, institutions, and nations interact with knowledge and information. Beyond its promise to revolutionize decision-making and productivity, artificial intelligence (AI) presents difficult problems for intellectual security, which protects knowledge integrity, autonomous thought, and freedom from manipulation. The problem is made much more urgent in Nigeria, where there is a disparity in digital literacy and AI policy frameworks are still developing. Therefore, this study explored strategies for balanced AI use, highlighting the importance of strong ethical frameworks, legal limitations, and public education campaigns. The study adopted a convergent parallel mixed-method design, combining quantitative surveys with qualitative interviews for triangulation. Surveys and interviews were conducted with 300 respondents and 15 key informants across Osun, Lagos, and Abuja with the help of three research assistants. A structured questionnaire and semi-structured interview guide were used to collect information from the respondents. The quantitative data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, and the qualitative data were analyzed thematically using NVivo 12 software. Results showed strong perceptions of AI’s benefits in information access and productivity but also concerns over misinformation and data manipulation. It was concluded that AI is a reflection of its design and is neither good nor harmful. This research is significant because it provides a balanced inquiry into AI’s benefits and risks, offering evidence-based insights to guide policymakers, educators, and society in navigating an AI-driven future. It alsoenriches debates in AI ethics and digital sociology by framing AI as both a cognitive enabler and a potential manipulator.
References
Aldoseri, A., Al-Khalifa, K. N., & Hamouda, A. M. (2024). AI-powered innovation in digital transformation: Key pillars and industry impact. Sustainability, 16(5), 1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16051790
Alotaibi, S. M. F. (2025). Determinants of Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) adoption among university students and its impact on academic performance: the mediating role of trust in technology. Interactive Learning Environments, 1-30. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2025.2492785
Al-Suqri, M. N., & Gillani, M. (2022). A comparative analysis of information and artificial intelligence toward national security. IEEE Access, 10, 64420-64434. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3183642
Bakiner, O. (2023). The promises and challenges of addressing artificial intelligence with human rights. Big Data & Society, 10(2), 20539517231205476. https://doi.org/10.1177/20539517231205476
Bécue, A., Praça, I., & Gama, J. (2021). Artificial intelligence, cyber-threats and Industry 4.0: Challenges and opportunities. Artificial intelligence review, 54(5), 3849-3886.
Biagini, G. (2025). Towards an AI-Literate Future: A systematic literature review exploring education, ethics, and applications. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 1-51. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-025-00466-w
Brennen, J. S., Simon, F., Howard, P. N., & Nielsen, R. K. (2020). AI and the news: Misinformation and automated journalism. Digital Journalism, 8(7), 870-889. https://doi.org/10.1080/21670811.2020.1732310
Burrell, J. (2016). How the machine ‘thinks’: Understanding opacity in machine learning algorithms. Big data & society, 3(1), 2053951715622512. https://doi.org/10.1177/2053951715622512
Chesney, R., & Citron, D. (2019). Deepfakes and the new disinformation war: The coming age of post-truth geopolitics. Foreign Aff., 98, 147.
Ferrara, E. (2024). The butterfly effect in artificial intelligence systems: Implications for AI bias and fairness. Machine Learning with Applications, 15, 100525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mlwa.2024.100525
Floridi, L. (2021). Establishing the rules for building trustworthy AI. In Ethics, governance, and policies in artificial intelligence (pp. 41-45). Cham: Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-81907-1_4
Gerlich, M. (2025). AI tools in society: Impacts on cognitive offloading and the future of critical thinking. Societies, 15(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/soc15010006
Habbal, A., Ali, M. K., & Abuzaraida, M. A. (2024). Artificial Intelligence Trust, risk and security management (AI trism): Frameworks, applications, challenges and future research directions. Expert Systems with Applications, 240, 122442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.122442
Hashmi, E., Yamin, M. M., & Yayilgan, S. Y. (2025). Securing tomorrow: a comprehensive survey on the synergy of Artificial Intelligence and information security. AI and Ethics, 5(3), 1911-1929. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43681-024-00529-z
Hermann, I. (2023). Artificial intelligence in fiction: between narratives and metaphors. AI & society, 38(1), 319-329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00146-021-01299-6
Kanchon, M. K. H., Sadman, M., Nabila, K. F., Tarannum, R., & Khan, R. (2024). Enhancing personalized learning: AI-driven identification of learning styles and content modification strategies. International Journal of Cognitive Computing in Engineering, 5, 269-278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcce.2024.06.002
Kolade, O., & Owoseni, A. (2022). Employment 5.0: The work of the future and the future of work. Technology in Society, 71, 102086. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2022.102086
Lewandowsky, S., Ecker, U. K., Seifert, C. M., Schwarz, N., & Cook, J. (2012). Misinformation and its correction: Continued influence and successful debiasing. Psychological science in the public interest, 13(3), 106-131. https://doi.org/10.1177/1529100620948940
Mitchell, M., Wu, S., Zaldivar, A., Barnes, P., Vasserman, L., Hutchinson, B., ... & Gebru, T. (2019). Model cards for model reporting. In Proceedings of the conference on fairness, accountability, and transparency (pp. 220-229). https://doi.org/10.1145/3287560.3287596
Obermeyer, Z., Powers, B., Vogeli, C., & Mullainathan, S. (2019). Dissecting racial bias in an algorithm used to manage the health of populations. Science, 366(6464), 447-453.
Păvăloaia, V. D., & Necula, S. C. (2023). Artificial intelligence as a disruptive technology—a systematic literature review. Electronics, 12(5), 1102. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12051102
Saeidnia, H. R., Hosseini, E., Lund, B., Tehrani, M. A., Zaker, S., & Molaei, S. (2025). Artificial intelligence in the battle against disinformation and misinformation: a systematic review of challenges and approaches. Knowledge and Information Systems, 67(4), 3139-3158.
Sarker, I. H., Furhad, M. H., & Nowrozy, R. (2021). Ai-driven cybersecurity: an overview, security intelligence modeling and research directions. SN Computer Science, 2(3), 173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-021-00557-0
Sarsia, P., Munshi, A., Joshi, A., Pawar, V., & Shrivastava, A. (2023). The Waning Intellect Theory: A Theory on Ensuring Artificial Intelligence Security for the Future. Engineering Proceedings, 59(1), 60.
Shin, D., Hameleers, M., Park, Y. J., Kim, J. N., Trielli, D., Diakopoulos, N., ... & Baumann, S. (2022). Countering algorithmic bias and disinformation and effectively harnessing the power of AI in media. Journalism & Mass Communication Quarterly, 99(4), 887-907. https://doi.org/10.1177/10776990221129245
Shoaib, M. R., Wang, Z., Ahvanooey, M. T., & Zhao, J. (2023). Deepfakes, misinformation, and disinformation in the era of frontier AI, generative AI, and large AI models. In 2023 international conference on computer and applications (ICCA) (pp. 1-7). IEEE.
Spector, J. M., & Ma, S. (2019). Inquiry and critical thinking skills for the next generation: from artificial intelligence back to human intelligence. Smart Learning Environments, 6(1), 1-11.
Suryanarayana, K. S., Kandi, V. P., Pavani, G., Rao, A. S., Rout, S., & Krishna, T. S. R. (2024). Artificial intelligence enhanced digital learning for the sustainability of education management system. The Journal of High Technology Management Research, 35(2), 100495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hitech.2024.100495
Tanikonda, A., Pandey, B. K., Peddinti, S. R., & Katragadda, S. R. (2022). Advanced AI-driven cybersecurity solutions for proactive threat detection and response in complex ecosystems. Journal of Science & Technology, 3(1).
Tlili, A., Zhang, J., Papamitsiou, Z., Manske, S., Huang, R., Kinshuk, & Hoppe, H. U. (2021). Towards utilising emerging technologies to address the challenges of using Open Educational Resources: a vision of the future. Educational Technology Research and Development, 69(2), 515-532. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-021-09993-4
Villegas-Ch, W., & García-Ortiz, J. (2023). Toward a comprehensive framework for ensuring security and privacy in artificial intelligence. Electronics, 12(18), 3786. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12183786
Yekollu, R. K., Bhimraj Ghuge, T., Sunil Biradar, S., Haldikar, S. V., & Farook Mohideen Abdul Kader, O. (2024). AI-driven personalized learning paths: Enhancing education through adaptive systems. In International Conference on Smart data intelligence (pp. 507-517). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-3191-6_38
Zhang, X., & Ghorbani, A. A. (2020). An overview of online fake news: Characterization, detection, and discussion. Information Processing & Management, 57(2), 102025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2019.03.004
Zuboff, S. (2023). The age of surveillance capitalism. In Social theory re-wired (pp. 203-213). Routledge.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Oparinde Olayiwola Raheef, Shina Olawale Olayiwola; Lawrence Oni A.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.

























