Learning Transformation: Effective Strategies for Transforming Ordinary Elementary School Classrooms into Interactive Math Labs
https://doi.org/10.51574/ijrer.v5i1.4278
Keywords:
Classroom Action Research, Elementary School, Interactive Learning, Learning Environment Transformation, Mathematics LaboratoryAbstract
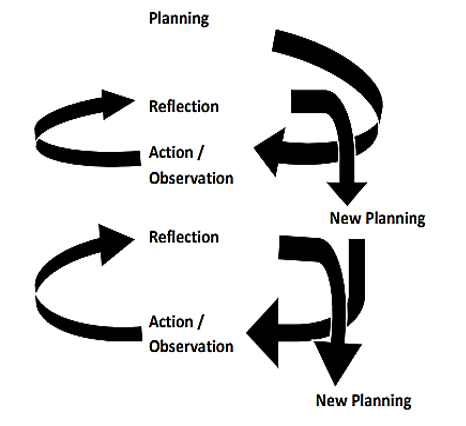
Textbook lectures and exercises typically dominate elementary school mathematics, which diminishes student enthusiasm and conceptual understanding. Students have trouble applying arithmetic to real life in non-visual, kinesthetic classrooms. Thus, this project seeks to create and implement a plan to turn primary school classrooms into engaging mathematics laboratories at SPF Unit of Tidung State Elementary School. Students' active participation and conceptual mastery of math are the goals. This study employs two cycles of Classroom Action Research (CAR). The transformation strategy includes 1) creating a Mathematics Corner with manipulatives, 2) using classroom walls as interactive visual media (posters and mind maps), and 3) implementing a Project-Based Learning (PjBL) Model in the new classroom. Monitoring student involvement, learning outcome tests, and student and instructor reaction questionnaires provided data. The study found that the transformation strategy provided an active and responsive learning environment. Student participation in mathematical exploration activities rose from 65% in cycle I to 88% in cycle II. Environmental intervention increased conceptual understanding by 15%. Mathematics was more appealing to students. This study demonstrates to primary schools, particularly those in urban areas, how to transform limited classroom space into a math laboratory without incurring significant costs. Its theoretical contribution strengthens empirical evidence that an interacting physical environment motivates and increases primary school pupils' math achievement.
References
Aboraya, W. (2021). Assessing students’ learning of abstract mathematical concepts in a blended learning environment enhanced with a web-based virtual laboratory. Journal of E-Learning and Knowledge Society, 17(3), 50-58. http://je-lks.org/ojs/index.php/Je-LKS_EN/article/view/1135520
Almarashdi, H. S., & Jarrah, A. M. (2022). The impact of a proposed mathematics enrichment program on UAE students’ mathematical literacy based on the PISA framework. Sustainability, 14(18), 11259. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141811259
Bayirli, E. G., Kaygun, A., & Öz, E. (2023). An analysis of PISA 2018 mathematics assessment for Asia-Pacific countries using educational data mining. Mathematics, 11(6), 1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11061318
Coffey, P., & Sharpe, R. (2023). An investigation into the teaching of numeracy in subjects other than mathematics across the curriculum. International Journal of Mathematical Education in Science and Technology, 54(5), 860-887. https://doi.org/10.1080/0020739X.2021.1978570
Daucourt, M. C., Napoli, A. R., Quinn, J. M., Wood, S. G., & Hart, S. A. (2021). The home math environment and math achievement: A meta-analysis. Psychological bulletin, 147(6), 565. https://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000330
De Vita, M., Verschaffel, L., & Elen, J. (2018). Towards a better understanding of the potential of interactive whiteboards in stimulating mathematics learning. Learning Environments Research, 21(1), 81-107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10984-017-9241-1
Durmaz, B. (2025). Learning Mathematics in School Spaces Outside the Classroom. In Mathematics Beyond the Classroom: A Guide for Expansive Learning in Out-of-School Environments (pp. 17-41). Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-032-05318-3_2
Gashaj, V., Thaqi, Q., Mast, F. W., & Roebers, C. M. (2023). Foundations for future math achievement: Early numeracy, home learning environment, and the absence of math anxiety. Trends in Neuroscience and Education, 33, 100217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tine.2023.100217
Hwang, G. J., Wang, S. Y., & Lai, C. L. (2021). Effects of a social regulation-based online learning framework on students’ learning achievements and behaviors in mathematics. Computers & Education, 160, 104031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2020.104031
Juan, Y. K., & Chen, Y. (2022). The influence of indoor environmental factors on learning: An experiment combining physiological and psychological measurements. Building and Environment, 221, 109299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2022.109299
Kaminski, J. A., & Sloutsky, V. M. (2020). The use and effectiveness of colorful, contextualized, student-made material for elementary mathematics instruction. International Journal of STEM Education, 7(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40594-019-0199-7
Kemmis, S., McTaggart, R., & Nixon, R. (2013). Introducing critical participatory action research. The action research planner: Doing critical participatory action research, 1-31. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-4560-67-2_1
Lambright, K. (2024). The effect of a teacher’s mindset on the cascading zones of proximal development: A systematic review. Technology, Knowledge and Learning, 29(3), 1313-1329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10758-023-09696-0
Lovianova, I. V., Kaluhin, R. Y., Kovalenko, D. A., Rovenska, O. G., & Krasnoshchok, A. V. (2022, June). Development of logical thinking of high school students through a problem-based approach to teaching mathematics. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series (Vol. 2288, No. 1, p. 012021). IOP Publishing. https://doi.org/ 10.1088/1742-6596/2288/1/012021
Loyens, S. M., Van Meerten, J. E., Schaap, L., & Wijnia, L. (2023). Situating higher-order, critical, and critical-analytic thinking in problem-and project-based learning environments: A systematic review. Educational Psychology Review, 35(2), 39. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-023-09757-x
Maschietto, M., & Trouche, L. (2010). Mathematics learning and tools from theoretical, historical and practical points of view: the productive notion of mathematics laboratories. ZDM, 42(1), 33-47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11858-009-0215-3
McKenzie, W. A., Perini, E., Rohlf, V., Toukhsati, S., Conduit, R., & Sanson, G. (2013). A blended learning lecture delivery model for large and diverse undergraduate cohorts. Computers & Education, 64, 116-126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2013.01.009
Mohammad, N., Nica, M., Levere, K. M., & Okner, R. (2023). Promoting engagement via engaged mathematics labs and supportive learning. International Electronic Journal of Mathematics Education, 18(2), em0732. https://doi.org/10.29333/iejme/12960
Mutodi, P., & Mosimege, M. (2021). Learning mathematical symbolization: Conceptual challenges and instructional strategies in secondary schools. Bolema: Boletim de Educação Matemática, 35, 1180-1199. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-4415v35n70a29
Nanda, A., & Rani, R. (2025). Exploring the proficiency of basic mathematical facts among primary mathematics teachers. Asian Journal for Mathematics Education, 4(1), 31-55. https://doi.org/10.1177/27527263241307975
Novikasari, I., Rahmawati, L., & Elebiary, N. (2024). Exploration of conceptual understanding and values in mathematics among prospective mathematics teachers. Union: Jurnal Ilmiah Pendidikan Matematika, 12(2), 331-339. https://doi.org/10.30738/union.v12i2.17714
Sartika, S. B., Efendi, N., & Rocmah, L. I. (2020). Pelatihan penggunaan laboratorium virtual bagi guru IPA dan matematika di SMP Sepuluh Nopember Sidoarjo. Dedication: Jurnal Pengabdian Masyarakat, 4(2), 201-208. https://jurnal.unipar.ac.id/index.php/dedication/article/view/368
Syaripah, S. (2021). Desain Pembelajaran Matematika Berbasis Etnomatematika untuk Menjadikan Laboratorium Matematika yang Inovatif Di IAIN Curup. Logaritma: Jurnal Ilmu-ilmu Pendidikan dan Sains, 9(01), 33-52. https://jurnal.uinsyahada.ac.id/index.php/LGR/article/view/3714
Udin, T., & Arfanaldy, S. R. (2025). Literature Analysis on Active Learning Models as an Alternative to the Dominance of Lecture Methods in Public Elementary Schools. Edu Cendikia: Jurnal Ilmiah Kependidikan, 5(01), 23-32. https://doi.org/10.47709/educendikia.v5i01.5674
Veraksa, N., Colliver, Y., & Sukhikh, V. (2022). Piaget and Vygotsky’s play theories: The profile of twenty-first-century evidence. In Piaget and Vygotsky in XXI century: Discourse in early childhood education (pp. 165-190). Cham: Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-05747-2_10
Waswa, D. W., & Al-Kassab, M. M. (2022). Mathematics learning challenges and difficulties: A students’ perspective. In International conference on mathematics and computations (pp. 311-323). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-0447-1_27
Wijaya, T. T., Hidayat, W., Hermita, N., Alim, J. A., & Talib, C. A. (2024). Exploring contributing factors to PISA 2022 mathematics achievement: Insights from Indonesian teachers. Infinity Journal, 13(1), 139-156. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v13i1.p139-156
Williams, M. P. (2022). Becoming an international public intellectual: Maria Montessori before the Montessori Method, 1882-1912. British Journal of Educational Studies, 70(5), 575-590. https://doi.org/10.1080/00071005.2022.2108757
Xi, J., & Lantolf, J. P. (2021). Scaffolding and the zone of proximal development: A problematic relationship. Journal for the Theory of Social Behaviour, 51(1), 25-48. https://doi.org/10.1111/jtsb.12260
Zajda, J. (2021). Constructivist learning theory and creating effective learning environments. In Globalisation and education reforms: Creating effective learning environments (pp. 35-50). Cham: Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-71575-5_3
Zandvliet, D. B., & Straker, L. M. (2001). Physical and psychosocial aspects of the learning environment in information technology rich classrooms. Ergonomics, 44(9), 838-857. https://doi.org/10.1080/00140130117116
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Latri Latri, Agusalim Juhari

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.

























