Problem-Based Learning Model Using Geogebra Application: Students Motivation to Learn Translation Material of High School
https://doi.org/10.51574/ijrer.v4i3.3473
Keywords:
GeoGebra, Learning Motivation, Problem-Based Learning, TranslationAbstract
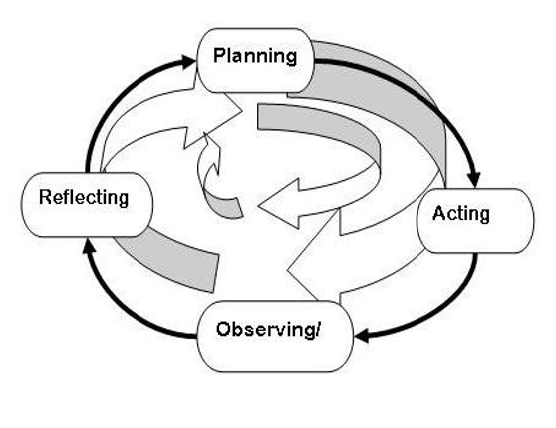
This study aims to describe the application of the Problem-Based Learning (PBL) model with the help of the GeoGebra application to increase students' learning motivation for geometric transformation material, especially translation. This study is a form of classroom action research carried out in two cycles in class XI E of High School 4 Palu involving 35 students. Each cycle consists of planning, implementation, observation, and reflection steps. In cycle I, the material is related to translation to points, while in cycle II, it is related to translation to lines. Data were collected through a learning motivation questionnaire and observation sheets, which were analyzed descriptively. The results indicated that students' learning motivation increased from cycle I to cycle II. In cycle I, only 6 students (17.1%) were included in the strong motivation category, while 11 students (31.5%) were included in the low category. After the improvement in Cycle II, the number of highly motivated students increased to 15 (42.8%), while those in the low group decreased to only 2 (5.8%). Observational data shows increased student engagement and enjoyment in learning. Consequently, the implementation of the GeoGebra-assisted PBL paradigm has proven successful in increasing motivation in mathematics learning.
References
Albrecht, J. R., & Karabenick, S. A. (2018). Relevance for learning and motivation in education. The Journal of Experimental Education, 86(1), 1-10.
Boadu, S. K., & Bonyah, E. (2024). The role of philosophy of mathematics education in mathematics teacher education. Cogent Education, 11(1), 2433832.
Cavilla, D. (2017). The effects of student reflection on academic performance and motivation. Sage Open, 7(3), 2158244017733790.
Dahal, N., Pant, B. P., Shrestha, I. M., & Manandhar, N. K. (2022). Use of GeoGebra in teaching and learning geometric transformation in school mathematics. Int. J. Interact. Mob. Technol., 16(8), 65-78.
Dolapcioglu, S., & Doğanay, A. (2022). Development of critical thinking in mathematics classes via authentic learning: an action research. International Journal of Mathematical Education in Science and Technology, 53(6), 1363-1386.
Handayani, E. D., Kusnawati, E., Sari, N. M., Yaniawati, P., & Zulkarnaen, M. I. (2022). Implementation of geogebra-assisted creative problem-solving model to improve problem solving ability and learning interest students. Al-Jabar: Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 13(1), 33-48.
Harun, N. F., Yusof, K. M., Jamaludin, M. Z., & Hassan, S. A. H. S. (2012). Motivation in problem-based learning implementation. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 56, 233-242.
Hohenwarter, M., & Jones, K. (2007). Ways of linking geometry and algebra, the case of Geogebra. Proceedings of the British Society for research into Learning Mathematics, 27(3), 126-131.
Ji, X., & Zheng, X. (2025). Can pedagogical agents and visual cues enhance students’ deep learning in a virtual reality environment? Insights from multiple data analysis. Education and Information Technologies, 1-23.
Jia, X. H., & Tu, J. C. (2024). Towards a new conceptual model of AI-enhanced learning for college students: The roles of artificial intelligence capabilities, general self-efficacy, learning motivation, and critical thinking awareness. Systems, 12(3), 74.
Kurniawan, R., Putra, A., & Dewi, F. (2023). Pengaruh motivasi belajar terhadap prestasi matematika siswa SMA. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika dan Sains, 11(1), 55–63.
LaForce, M., Noble, E., & Blackwell, C. (2017). Problem-based learning (PBL) and student interest in STEM careers: The roles of motivation and ability beliefs. Education Sciences, 7(4), 92.
Li, J., & Xue, E. (2023). Dynamic interaction between student learning behaviour and learning environment: Meta-analysis of student engagement and its influencing factors. Behavioral Sciences, 13(1), 59.
Loh, E. K. (2019). What we know about expectancy-value theory, and how it helps to design a sustained motivating learning environment. System, 86, 102119.
Nurfadilah, U., & Suhendar, U. (2018). Pengaruh penggunaan GeoGebra terhadap kemampuan pemecahan masalah siswa pada topik garis dan sudut. JMPM: Jurnal Matematika Dan Pendidikan Matematika, 3(2), 99-107.
Puspasari, A., Hidayat, R. A., & Wahyuningsih, I. (2023). Peningkatan Motivasi Belajar Menggunakan Model Problem Based Learning (PBL) Dengan Metode Make A Match Dalam Muatan PPKn Di Kelas II SDN Tamansari 3. Prosiding Seminar Nasional Pendidikan Profesi Guru (Vol. 2, No. 1, pp. 835-839).
Schweder, S., & Raufelder, D. (2024). Does changing learning environments affect student motivation?. Learning and Instruction, 89, 101829.
Schoenfeld, A. H. (2022). Why are learning and teaching mathematics so difficult?. In Handbook of cognitive mathematics (pp. 1-35). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Shin, M., & Bolkan, S. (2021). Intellectually stimulating students’ intrinsic motivation: the mediating influence of student engagement, self-efficacy, and student academic support. Communication Education, 70(2), 146-164.
Waheed, M., Kaur, K., Ain, N., & Hussain, N. (2016). Perceived learning outcomes from Moodle: An empirical study of intrinsic and extrinsic motivating factors. Information Development, 32(4), 1001-1013.
Wulandari, W., & Misu, L. (2023). Problem-Based Learning Model with Geogebra Support on Students' Ability to Solve Mathematical Problems. Jurnal Amal Pendidikan, 4(3), 240-250.
Yohannes, A., & Chen, H. L. (2023). GeoGebra in mathematics education: a systematic review of journal articles published from 2010 to 2020. Interactive Learning Environments, 31(9), 5682-5697.
Zaccone, M. C., & Pedrini, M. (2019). The effects of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation on students learning effectiveness. Exploring the moderating role of gender. International Journal of Educational Management, 33(6), 1381-1394.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Nurfadila Nurfadila, Muh. Hasbi, Ni Made Puspawati

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.

























